Hadrian’s Wall – The History and Purpose of Hadrian’s Wall
Hadrian’s Wall is one of the most famous pieces of Roman architecture in the world, and definitely the most famous instance of this famous civilization within England. We are going to look at the general history, construction, occupation, and influence of this famous Roman wall in England over the course of this article. Keep reading to learn more about Hadrian’s Wall!
Contents
A Look at Hadrian’s Wall
| Architect | Hadrian (76 – 138 CE) |
| Date Constructed | 122 – 128 CE (Approximately) |
| Function | Defensive fortification |
| Materials Used | Stone, wood, and turf |
| Length | 117 km (or 73 mi) |
| Location | Northern England, United Kingdom |
The history of many European and Northern African countries intersects with the history of the Roman Empire. The Romans were prolific conquerors and they spread their influence throughout the world with incredible tenacity and capability. This empire maintained its hold over various territories for centuries before it finally split in two, morphed into a new empire, and eventually morphed even further into a new Holy Roman Empire, before eventually coming to a complete end. The history of Rome is long and multi-faceted, and the history of Rome is not solely found in Italy or just Rome. One of the places that the Romans did conquer but lost earlier than many of the other regions that they would eventually lose, was England. Various remnants of Roman civilization can be found throughout England, and one of those remnants is Hadrian’s Wall.
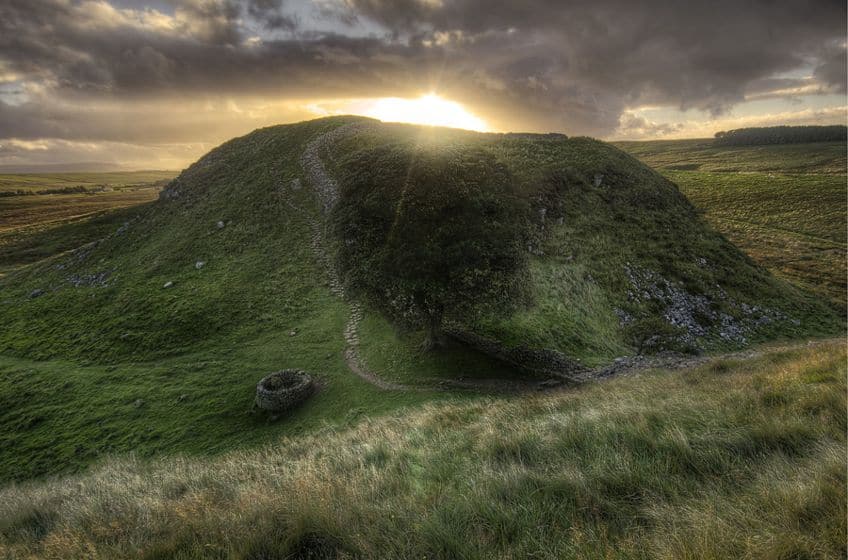

Hadrian’s Wall, as the name may suggest, was named after the Roman Emperor of the same name, and this Roman wall in England has a similarly long history. But just where is Hadrian’s Wall today? Where can it be found? Much of it no longer exists because it is a truly ancient structure, but pieces of it span across Northern England to this day. So, let’s have a look at this Roman wall in England to see why it has remained such a famous piece of Roman architecture over the course of so many centuries.
The History of Hadrian’s Wall
When asking questions about Hadrian’s Wall, like: where was Hadrian’s Wall built or how long is Hadrian’s Wall, it is important to note something about it. It is worth remembering that much of Hadrian’s Wall no longer actually exists, as it “celebrated” its 1900-year birthday in 2022, and so this is a truly ancient structure. Much of it is long gone, and the reasons for which it was built are also long-gone.
We do not know everything we may want to know about this ancient Roman wall in England, but we can attempt to know and understand as much as we can know.
This means that certain aspects of the construction and history of Hadrian’s Wall architecture and its general existence are products of archaeology and educated speculation. We do not know everything we want to know about it. So, everything in the remainder of this article should, at times, be taken with that in consideration. We know as much as we can know through studying this ancient wall, but that does not mean that we will be particularly successful in doing that. Without further ado, what is Hadrian’s Wall and how was it built?
Construction of the Wall
We know that Hadrian’s Wall took at least six years to construct, and that construction would have started at around 122 CE. We know this because that was the year that Emperor Hadrian visited England and ordered its construction. The supposed architect of the wall was the emperor himself, but as it was mostly a wall and did not include anything necessarily complex in its general construction, it may be easiest to say that it was constructed with less skill than something like the Pantheon in Rome. The wall itself was built by the Roman military, and as there were about 15,000 Roman troops in the region at the time, this would serve as a good, disciplined, and capable workforce for constructing a defensive wall such as this. This also allowed the wall to maintain a militaristic air from the beginning of its construction until the end of it.
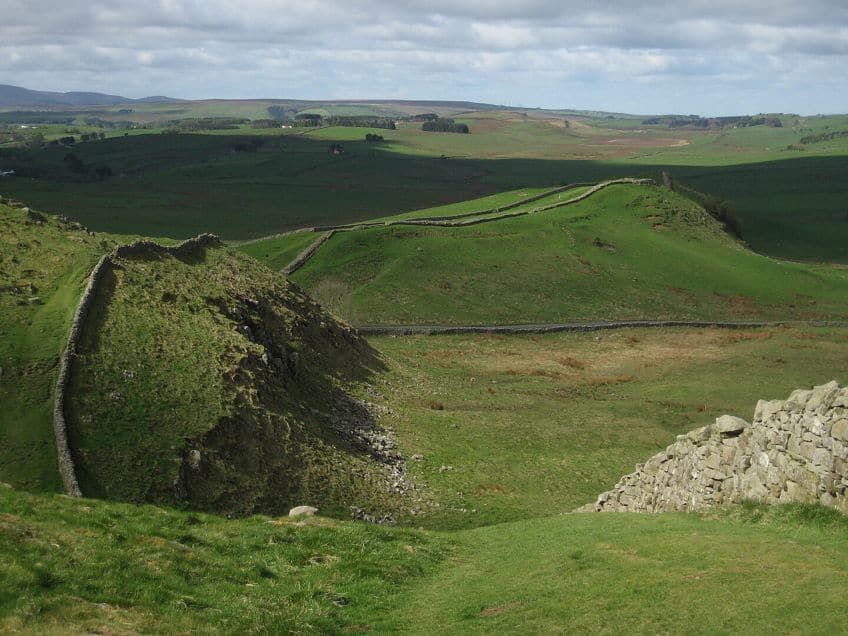

This stone wall was eventually completed, and it ran the full length of the country. It started in Wallsend in the east of the country until Bowness-on-Solway in the west. This means that Hadrian’s Wall spanned the length of England. So, how long was Hadrian’s Wall? Well, it was 117 km (or 73 mi). This is an utterly gargantuan construction that, despite it not being one of the more sophisticated Roman structures to have been built, its sheer scope makes it one of the most impressive ever constructed.
Purpose and Intention of the Wall
Why was Hadrian’s Wall built? Why are most walls of this nature built? It was a defensive perimeter. The idea was quite basic. The Romans had been skirmishing against some of the so-called “barbaric” tribes to the north, such as the Scots, and they wanted to protect Britannia, which was the Roman-controlled province in the region. This wall allowed them to add later layers of defense to aid in the defense of their own region while also allowing them to maintain control over those who were on their side of the wall. A distinctive border wall like this allowed the Romans to prevent anyone from easily fleeing their side of the country, and such a massively long wall meant that it would be difficult for anyone to evade capture. This served a good role as more than just defense, but also as a form of propaganda. It showed off the glorious might of the Roman Empire, specifically of Hadrian.
This wall allowed the Romans to maintain their own power and control the flow of any who may have wanted to pass across this border.
Political Context of the Wall’s Creation
This Roman wall in England was an immensely long structure that separated the Roman province of Britannia from the supposedly barbaric regions to the north, and because of this, the wall’s existence was likely planned before Hadrian’s famed visit to the region. There needed to be a way to maintain the empire, and as there had been issues in various provinces controlled by the Romans, it made sense for them to attempt to consolidate their power in the regions that they still held a tight grip over.
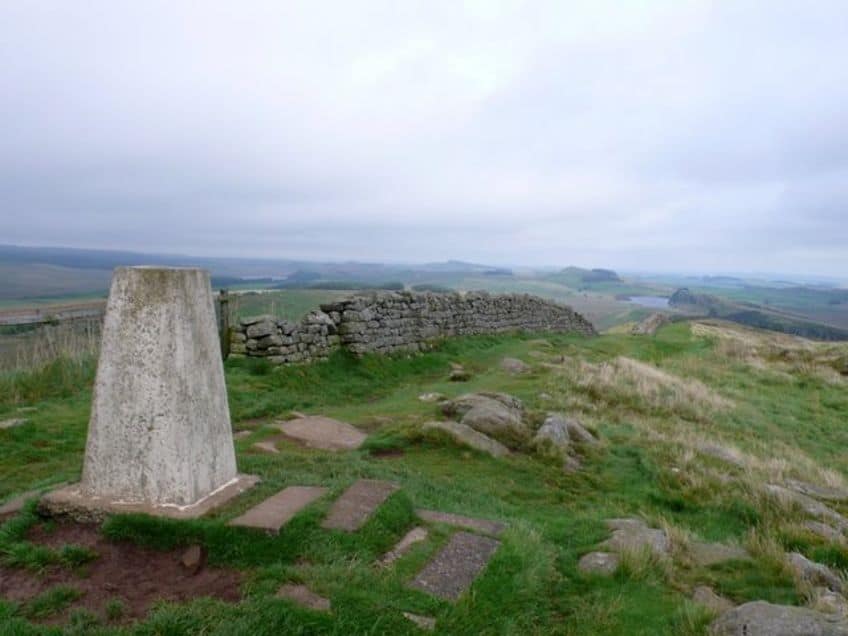

We do not know, and there is disagreement from academics, about whether the northern “barbarians” actually posed a real threat to the Romans, but constructing something like this serves well, as previously mentioned, as a piece of propaganda. This wall may not have been strictly necessary to maintain Roman control over the region, but it became a powerful symbol of the might and political ability of the Roman Empire as a whole.
The Design and Architecture of Hadrian’s Wall
As has been mentioned, Hadrian’s Wall was not merely for defense but existed as a statement of Roman power and authority. This Roman wall in England served as a separation between supposed civilization and barbarism. It was a powerful image too. It allowed the Romans to claim that their civilization was superior to all others, and they were able to keep their inhabitants within the confines of their province so that their claim could never be questioned.
However, what was significant about the Hadrian’s Wall architecture that allowed this to be the case?
Wall Measurements and Specifications
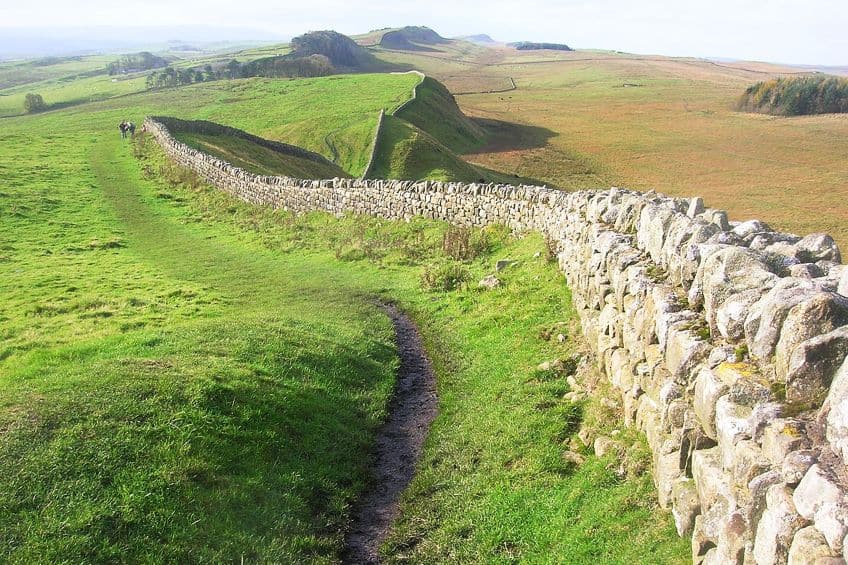
Hadrian’s Wall was long. We have already mentioned the length of this wall as 117 km (or 73 m), but how long was Hadrian’s Wall to the Romans? To them, this wall was 80 Roman miles and constructed to be 2.4 m (or 8 ft) thick along the length of the structure. In addition to this thickness, large ditches were built in front and behind the wall so that the soldiers stationed on it would have a far easier time defending against any who would attempt to scale it. Asking a question about the simple length of the wall misses the other impressive measurements that the wall adopted. Today, the wall is mostly in ruins, but according to a monk and historian who was alive when the wall still stood, the wall was supposedly about 3.7 m (or 12 ft) tall.
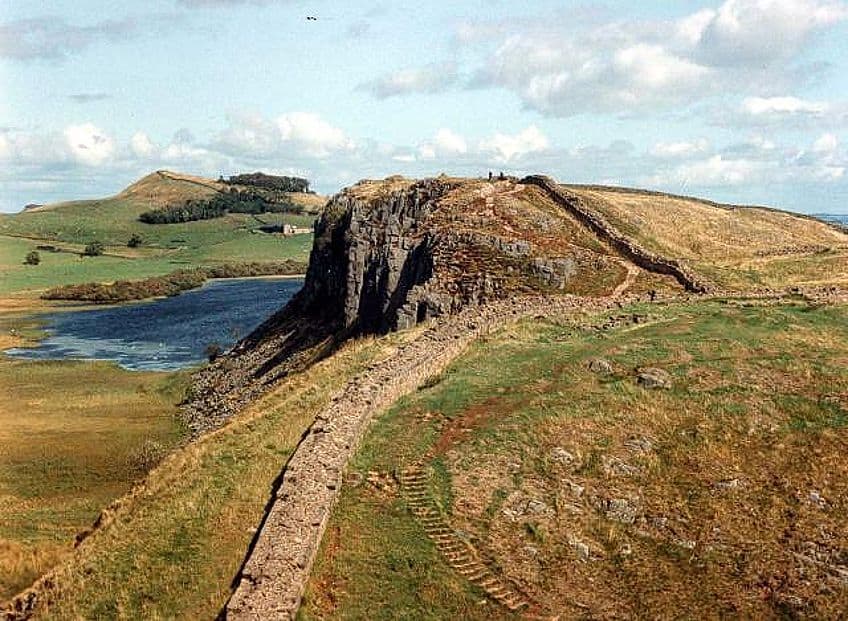

In addition to the width and height of this structure, Hadrian’s Wall also needed to serve as a place for soldiers to be stationed. A defensive position without defenders is just an inconvenience that needs to be climbed, and so there are also guard posts and watchtowers half a kilometer or so. This meant that the soldiers would always have a good view of the surrounding landscape while also having a place to live. This immense length, width, and height was an impressive sight to behold, and it was constructed from stone and wood.
Some of the areas that were initially made of wood were later replaced with stone, but much of this stone would eventually be taken from the site as the years dragged on and the Roman Empire fell into disarray and eventually entirely dissolved.
Forts and Structures Along the Wall
It has already been mentioned that there were various structures along Hadrian’s Wall, but these additional structures came in several types. There were mostly smaller guard posts and defensive turrets, but there were also several larger forts along the wall. These structures allowed Hadrian’s Wall to maintain its defensive position for centuries after it had been built. In addition to the forts themselves, the ditches that were dug around the wall aided in this defensive position, and one of the most interesting things about these pits is that they were covered in sharpened branches and thorns, which effectively acted as an ancient form of barbed wire. Hadrian’s Wall was a defensive position unlike practically all others at the time, and it would go on to have a massive influence on defensive walls made in the future.
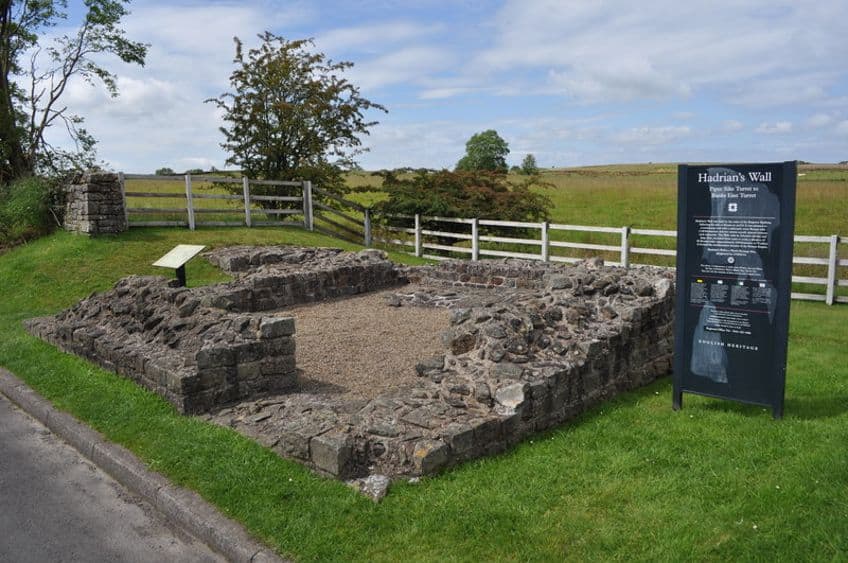

Building Materials and Techniques Used
Hadrian’s Wall was constructed, as has already been briefly mentioned, out of stone and the use of wood especially allowed the structure to be built far faster than may have otherwise been possible. However, as the wall became occupied, more portions of the wall were replaced with stone to increase the defensive capabilities of this Roman wall in England as a whole. There was also a section initially constructed out of turf but later replaced with stone. The wall was constructed in a comparatively simple way in comparison to some of the other Roman constructions of the period, but a wall requires a lessened architectural complexity to some of the other famous Roman architectural designs, like the continuous slope of aqueducts or the precision needed for the construction of domes.
The soldiers, many of whom were also engineers, carpenters, masons, and so on, would spend six years of their lives building this wall that would remain standing for centuries to come.
Life on Hadrian’s Wall
Hadrian’s Wall was occupied for several centuries, and it needed to be occupied by human beings who needed a place to live and a general way of life. So, what was this way of life and how did it proceed over the many years that the wall was occupied? Let’s have a look at that question.
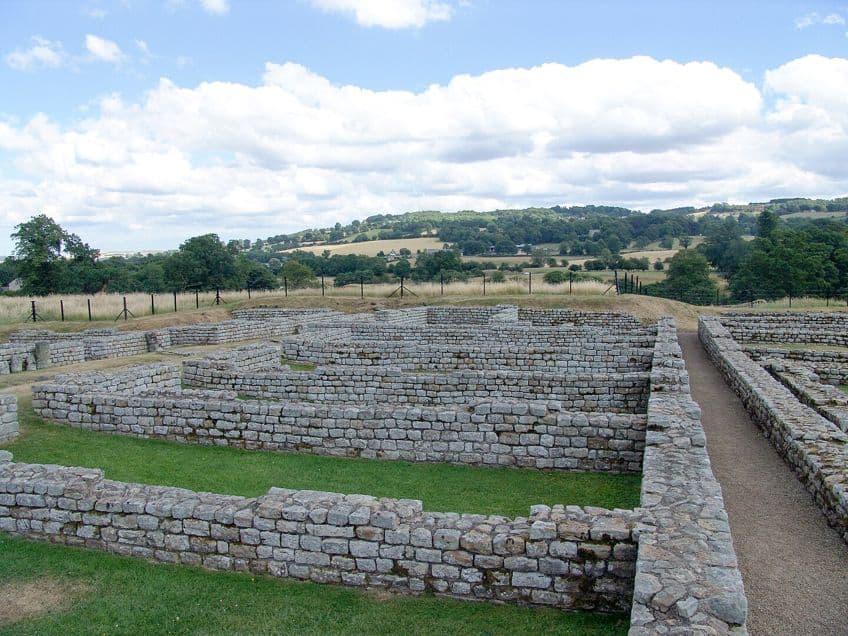

Daily Life for Soldiers Stationed on the Wall
The average soldier who was positioned on Hadrian’s Wall would typically patrol the wall along the top of the structure and also maintain a watch from the many forts and turrets along the way. At its height, the wall was occupied by about 10,000 soldiers who were taken from various auxiliary units in the Roman army. Defense was one of the primary purposes of the wall, but these soldiers were also likely expected to effectively serve as border patrol agents.
Hadrian’s Wall was, after all, a border wall that separated the Roman province of Britannia from the northern regions, but this did not mean that no one could ever leave, but one had to leave with an official purpose.
Interaction with Local Communities
Another interesting thing about this wall is that because of its high occupancy and its existence as a symbol of Roman power and authority, the region around the wall became occupied too. There were regions on either side of the wall that were occupied by farmers and townspeople. This meant that there was constant interaction between the local Britons and the Romans who manned the wall, and this led to some level of cultural exchange.
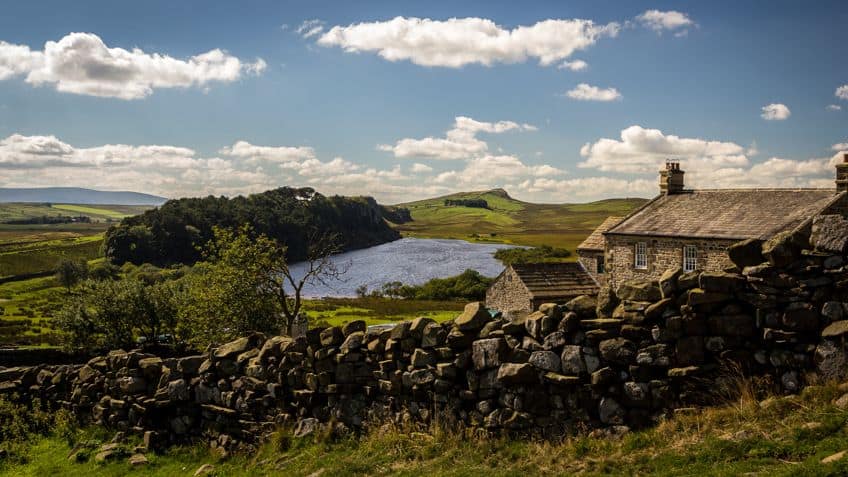

Evidence of Cultural Exchange
The Romans who lived in the region may have only accounted for a quarter to a third of the total population in the area, and so the local people would have also been quite prominent in the general area. This did also mean that as the Romans maintained hegemonic power in the region, many of the Britons in the area either assimilated into this way of life or, in some way, rebelled against it. This combination of rebellion and assimilation would be prominent in areas so close to direct Roman control, and this is one of the reasons that Roman influence held such a strong sway even in modern British culture.
The Roman Empire was clearly one of the powerhouses of the world and being in proximity to it led to inherent cultural exchange between Romans and the local peoples in the region.
The Decline and Abandonment of Hadrian’s Wall
Hadrian’s Wall, despite being a powerful symbol of Roman power, would eventually fall into disrepair and eventual abandonment. As any empire eventually crumbles so do its institutions. Hadrian’s Wall was abandoned centuries ago, and its abandonment led to its ultimate decline as a structure. But why did this happen?
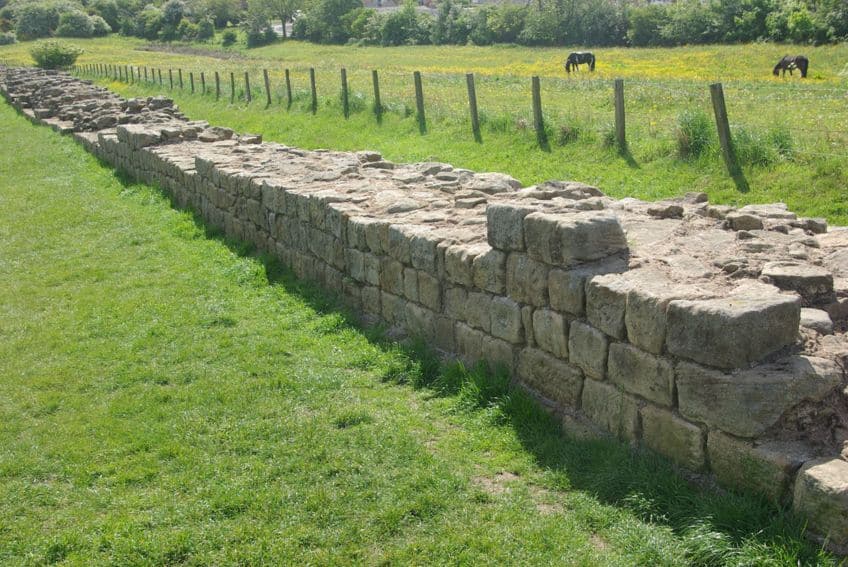

Reasons for the Wall’s Decline
Hadrian’s Wall was a cornerstone of the architectural might of Emperor Hadrian, but as soon as Hadrian was dead, his successor essentially relegated the structure to a support role. Instead, he built the Antonine Wall in modern-day Scotland to the north. This wall was nowhere near as famous as Hadrian’s Wall, but it was part of an attempt to conquer the northern tribes. This turned out to be a failure.
When Marcus Aurelius came to power, he then subsequently abandoned the Antonine Wall and moved to reuse Hadrian’s Wall instead.
This back and forth would continue as Hadrian’s Wall was abandoned, then the Antonine Wall was abandoned, and so on. Once the conquest of Britain stopped being a priority and the Romans left the country as a whole, the wall became unguarded and unoccupied. The locals did not use it to the same extent and so it gradually fell into decline.
Archaeological Evidence of the Wall’s Abandonment
Well, the most obvious sign of this is that Hadrian’s Wall is no longer patrolled. However, we know that as invasions and economic decline rocked the Roman Empire, the Romans effectively pulled out of Britain entirely. Some sections of the wall, according to archaeological evidence, may have been occupied into the 5th century, but after that, the wall was no longer a necessary defensive position.
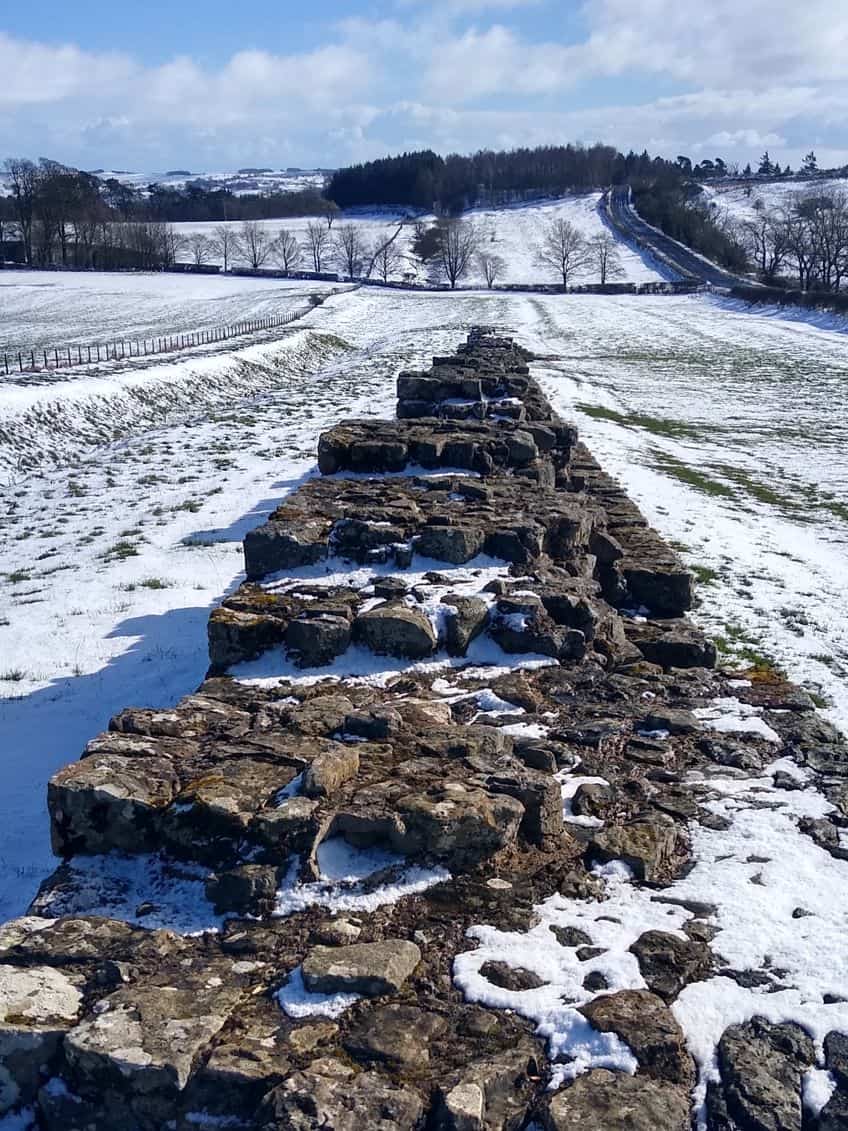

Some of the forms continued to be used far further into the future, but the cost and logistics necessary to maintain a wall that ran for over a hundred kilometers were too much for many of these civilizations to continue. So, the wall started to be dismantled by locals to use for various other projects. It was only in the 18th century after large swaths of the wall had been taken that someone tried to preserve what was left. This preservation proved to be successful, and Hadrian’s Wall does still stand to this day in part because of those preservation attempts. However, there have been other archaeological finds related to the wall, such as a 2021 discovery of 3 meters of previously undiscovered wall.
So, the story of Hadrian’s Wall is not necessarily over just yet.
Impact of the Wall on Subsequent History
Hadrian’s Wall would go on to have a large impact on various aspects of wall design and border defenses in subsequent centuries. In addition to this, Hadrian’s Wall had an influence on culture as a whole, as will be discussed below. So, let’s look at some of that modern impact and how this Roman wall in England has remained such a culturally significant landmark.
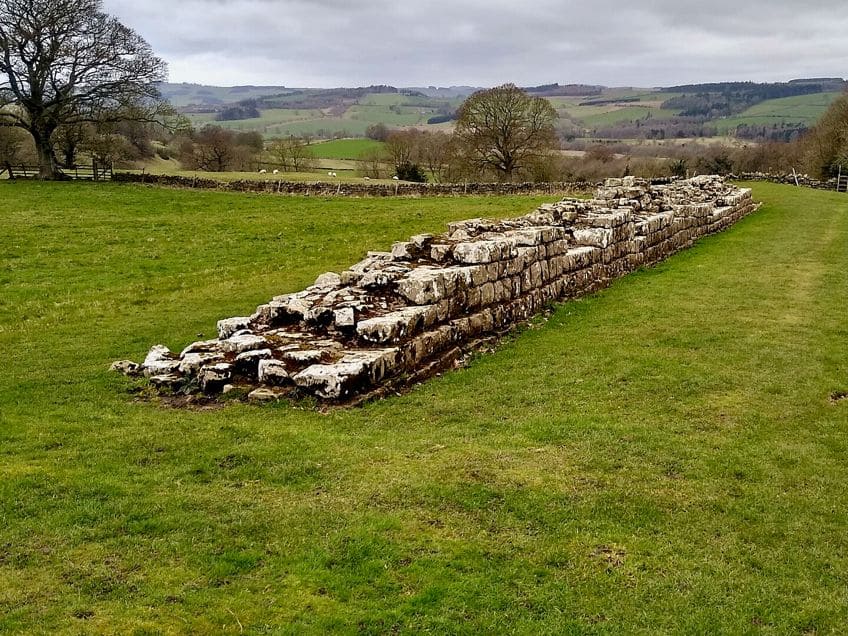

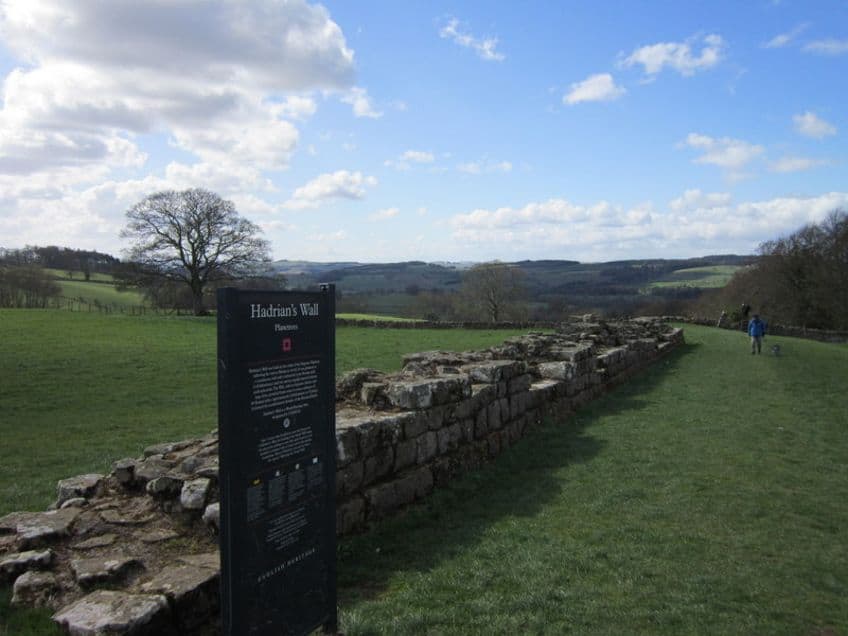
Visiting Hadrian’s Wall Today
Hadrian’s Wall can be visited to this day. It no longer holds any kind of a defensive function and, by modern military standards, is likely a rather quaint type of defense. This means that Hadrian’s Wall has effectively become a tourist spot in recent years. Some of the forts can still be visited, or at least those that are still standing, and the trail that runs along the length of the wall can be hiked or cycled.
The wall as a whole became a World Heritage Site in 1987, but regardless of its status, there is no dedicated protection for the site.
Unlike a building in a city, it can be rather difficult to maintain security guards along something that is over a hundred kilometers in length. This means that people can climb the wall, but the organization that maintains it requests that people don’t do that as it can ultimately damage this World Heritage Site. So, one can visit this wall, witness the decaying remnant of the Hadrian’s Wall architecture, pop in at a few of the forts along the way, and, in general, experience the location that once served as an ancient Roman defensive position. Hadrian’s Wall may not be in the prime state that it was once in, but it does still stand as a monument to what had once been possible in ancient cultures.
Hadrian’s Wall in Popular Culture
Hadrian’s Wall has been used in various pieces of popular culture over the years. This has been done in both direct and indirect ways. One does not necessarily need to use the wall itself in a piece of media to draw inspiration from it, so let’s have a look at a few of the examples of pieces of popular culture that have, in some way, been influenced by this famous Roman wall in England.
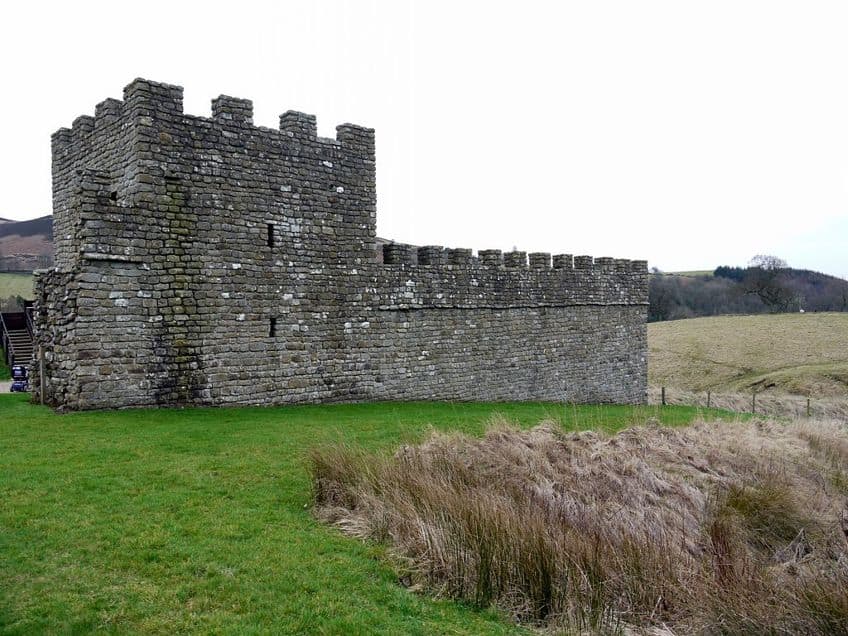

Literature and Film Featuring Hadrian’s Wall
Hadrian’s Wall can be found in prose, like the short stories of Rudyard Kipling, who used this wall as a stand-in for his “Great Pict Wall” in these narratives. There have also been films like the 2004 film King Arthur, which prominently features the wall as a major part of the narrative as a whole. There are even poems, like the W.H. Auden poem “Roman Wall Blues”, which was focused on the wall.
In the modern era, even interactive media has made use of the wall, and the Ubisoft-published game Assassin’s Creed Valhalla features Hadrian’s Wall as a location that can be visited.
These are simply examples of Hadrian’s Wall that have existed as direct forms of the wall, but this famous wall has also influenced fiction in a more indirect sense. George R.R. Martin has stated that Hadrian’s Wall played a large role in his inspiration for The Wall in the Game of Thrones series. If there’s a big wall like this in a piece of media, then it’s quite possible that Hadrian’s Wall played at least something of a role in its inspiration.
Popularity of the Wall as a Tourist Attraction
Hadrian’s Wall still exists as a tourist attraction, as has already been mentioned, and one can hike along the path beside the wall (or cycle beside it), take in a few stunning views from various locations along the wall, visit the various towns and defensive structures that were used during the height of the wall’s use, and even visit a few museums along the way that contain Roman artifacts from the period. Thanks to the wall’s incredible length, one does not even need to visit any of the official locations along the wall and one can simply visit it from the outside. It is impossible, for this reason, to also track how often the wall is visited. It’s not exactly a single building that can track admissions, after all.

Modern-Day Significance of the Wall
In the modern day, thanks to Roman history and architecture being such an integral aspect of Western history, Hadrian’s Wall has become an important piece of both Roman and British history. This wall is the largest and most famous piece of Roman architecture in England, and as such it has retained a level of significance befitting its place in world history.
The legacy of Hadrian’s Wall has been maintained to this day.
The Legacy of Hadrian’s Wall
Hadrian’s Wall may be famous today, but it was also famous in the past. It had a profound influence on various instances of world history and defensive architecture. Let’s have a look at some of that legacy below.

Influence on Later Border Defenses
As Hadrian’s Wall is, obviously, a defensive structure that served as an immensely effective means of keeping enemies out of the region, the influence of this wall on subsequent border defenses cannot be overstated. There were other Roman walls, such as the Limes Germanicus in Germany and the Antonine Wall in Scotland, that emulated the general design of Hadrian’s Wall. There have also been other large-scale wall defenses that used Hadrian’s Wall as a model, and as Roman architecture has had such a profound influence on Western architecture as a whole, it makes sense that others would seek to copy the Romans in terms of defensive strategies.
There is also something rather primal about constructing a big wall to keep people out, and the Romans tapped into this long before it became a political slogan in the 21st century.
Legacy in Art and Literature
As has already been mentioned, Hadrian’s Wall has served as an influence on various pieces of popular culture in recent decades, but it was also described and discussed in many ancient texts. Hadrian’s Wall has been portrayed, used as an influence, and directly copied in many pieces of art and literature over the millennia since it was constructed, and while the wall is mostly a shadow of its former self, it still exerts a powerful influence through the works that it has in turn influenced.
Importance of Hadrian’s Wall to Modern-Day Historians
Because of Hadrian’s Wall’s place as the largest piece of Roman architecture in England, it has served as an important part of Western history for the historians who wish to study that period. While there are few pieces of historical records from that period, the existence of the wall itself, and that pieces of it are still occasionally discovered, means that Hadrian’s Wall will likely remain one of the most important pieces of Roman history in the country.

We have come to the end of our discussion about Hadrian’s Wall. This famous Roman wall in England has become one of the most prominent instances of Roman architecture in Britain, and so we have spent this article looking at its general history, its existence in the modern era, and the influence that it exerted on the world after its construction. Hopefully, you learned a good deal from this discussion. So, all that’s left to say is that we hope you have a fantastic day ahead and perhaps manage to climb over a few walls of your own, but maybe make sure those walls don’t have security guards on the other side!
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is Hadrian’s Wall?
Hadrian’s Wall is an ancient Roman wall in England that served as a defensive fortification that ran along the length of the country. It was intended to keep the enemies of the Roman Empire out while keeping the citizens inside. It fell into disrepair over the centuries, but it still stands to this day, and that further shows the resilience of ancient Roman structures.
Where Was Hadrian’s Wall Built?
So, where is Hadrian’s Wall? It was constructed along the length of Northern England. To be more specific, it started in the east, in Wallsend, and continued to the west coast, in Bowness-on-Solway. This means that Hadrian’s Wall once spanned the entirety of the country. This was not some small wall, as it was massive in length and had an impressive width and height too.
How Long Was Hadrian’s Wall?
Hadrian’s Wall was 80 Roman miles in length. If you’re unfamiliar with Roman miles, it was 117 km (or 73 mi) in length. This is an absolutely massive stretch of land for any structure to cover, and because of this length, it is one of the longest walls in the world. Its massive length also means that large sections of it still exist, even though it is nearly two millennia old and wasn’t maintained for several centuries.
Justin van Huyssteen is a writer, academic, and educator from Cape Town, South Africa. He holds a master’s degree in Theory of Literature. His primary focus in this field is the analysis of artistic objects through a number of theoretical lenses. His predominant theoretical areas of interest include narratology and critical theory in general, with a particular focus on animal studies. Other than academia, he is a novelist, game reviewer, and freelance writer. Justin’s preferred architectural movements include the more modern and postmodern types of architecture, such as Bauhaus, Art Nouveau, Art Deco, Brutalist, and Futurist varieties like sustainable architecture. Justin is working for artfilemagazine as an author and content writer since 2022. He is responsible for all blog posts about architecture.
Learn more about Justin van Huyssteen and about us.
Cite this Article
Justin, van Huyssteen, “Hadrian’s Wall – The History and Purpose of Hadrian’s Wall.” artfilemagazine – Your Online Art Source. June 21, 2023. URL: https://artfilemagazine.com/hadrians-wall/
van Huyssteen, J. (2023, 21 June). Hadrian’s Wall – The History and Purpose of Hadrian’s Wall. artfilemagazine – Your Online Art Source. https://artfilemagazine.com/hadrians-wall/
van Huyssteen, Justin. “Hadrian’s Wall – The History and Purpose of Hadrian’s Wall.” artfilemagazine – Your Online Art Source, June 21, 2023. https://artfilemagazine.com/hadrians-wall/.