Paleolithic Art – Exploring the Early Art of Humanity
Paleolithic art is one of the most ancient forms of art that have ever been discovered. The history of cave paintings and that of ancient human culture are often conjoined with one another. In this article, we will examine the Paleolithic period, the different types of art that were created during this era, and a few specific instances of Paleolithic artworks. Keep reading to learn more about Paleolithic art!
Contents
- 1 A Look at Paleolithic Art
- 2 Types of Paleolithic Art
- 3 Examples of Paleolithic Artworks
- 3.1 Lion-man Sculpture (39,000 – 33,000 BCE) from Hohlenstein-Stadel
- 3.2 Chauvet-Pont-d’Arc Cave Paintings (Possibly 35,000 – 31,000 BCE) from Ardèche
- 3.3 Venus of Dolní Věstonice (29,000 – 25,000 BCE) from Dolní Věstonice
- 3.4 Cosquer Cave Paintings (25,000 – 17,000 BCE) from the Calanque de Morgiou
- 3.5 Lascaux Cave Paintings (15,000 BCE) from Dordogne
- 4 Frequently Asked Questions
A Look at Paleolithic Art
Let’s have a look at some Paleolithic art, but what does Paleolithic mean in the first place? This is a term that refers to a period of the Stone Age that only ended about 10,000 years ago. Some of the most common aspects of Paleolithic art that we have discovered are relatively rudimentary artworks generally painted or etched into caves or carved into small sculptures or carvings.
We still do not know the meaning of various examples of Paleolithic art, but we do know that it formed some part of Paleolithic culture. Art has formed part of human culture for the entirety of its existence, and ancient humans from 2.6 million to 10,000 years ago are no exception to that. Art is part of human existence and experience. The Paleolithic, regardless of how long ago it was, is the same.
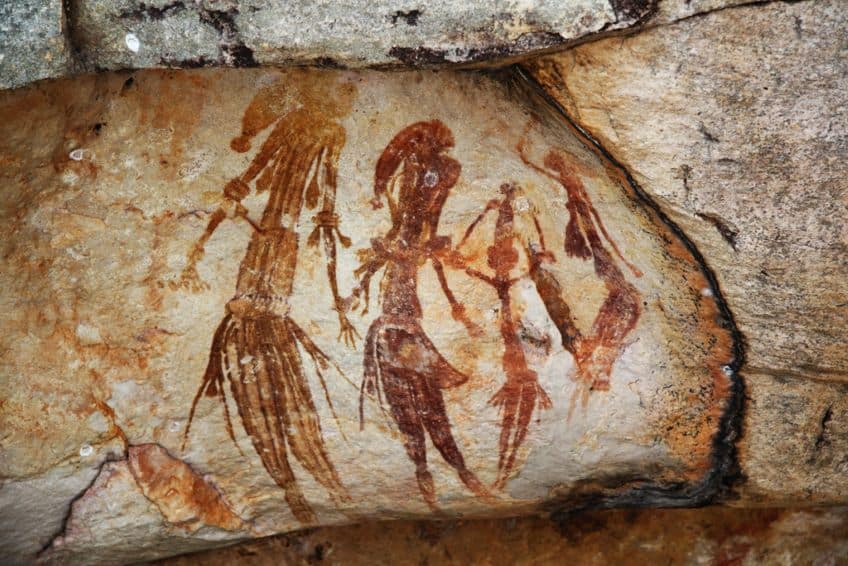

One of the distinguishing features of the Paleolithic period is that humans were able to use stone tools. This is also the time during which homo sapiens started to emerge. These early humans had language, culture, religion, and art, and this means that much of our origin begins during this period. However, it was only during the Neolithic period that we started farming, the Paleolithic period was when we were still living in nomadic hunter-gatherer societies.
However, we do not actually know the beliefs or culture of Paleolithic humans. We can only glean from contextual clues. We know they had tools, but they had no written language, and so there is no way to definitively learn anything about them in that sense. What did they believe in? We have no idea. Paleolithic art, on the other hand, is quite well-known because it is something that these early humans left behind for us. We can study them through what they created.
We know that they developed means of painting and drawing, of sculpting and carving, and they also learned how to mix certain types of pigments to create early paint.
In terms of the history of Paleolithic art, it can be generally divided into three main phases: the Lower Paleolithic art period (2.6 million to 250,000 years ago) which saw the use of simple tools with basic piercings and engraving being possible. Then there was the Middle Paleolithic art period (250,000 to 40,000 years ago) in which more refined tools were created, such as scrapers and blades. This allowed for the creation of beads and similar ornamentation. Lastly, the Upper Paleolithic art period (40,000 to 10,000 years ago) which led to the use of cave paintings, small sculptures, flutes, and ornaments. This is also the period during which humans developed far further in terms of culture. And that is the Paleolithic era and culture. However, we still need to look at actual Paleolithic art. Firstly, we need to look at some of the specific types of Paleolithic art before we examine some of the many tangible examples that we have found throughout the world.
Types of Paleolithic Art
There are many different types of Paleolithic art that are worth discussing. Let us quickly have a look at some of the different types of Paleolithic art before we examine a few tangible specific examples that we have discovered over the years.
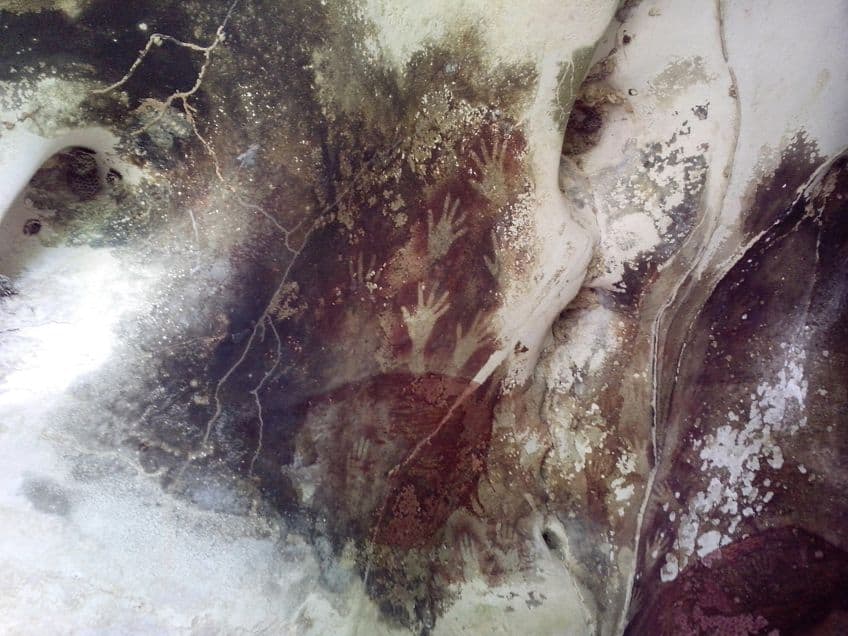
Paleolithic Drawings
Another of the forms that are quite common include Paleolithic drawings, and while these can be compared to paintings, there are certain differences. Many instances of rock art made use of paint, but the common image of hand stencil images in Paleolithic cave networks could be called drawings instead of paintings. In addition, cave walls were often carved or scratched with sharpened tools to allow for Paleolithic drawings to be created.
These carvings are often better at surviving the elements and so some of them can be found outside of caves.
Paleolithic Paintings
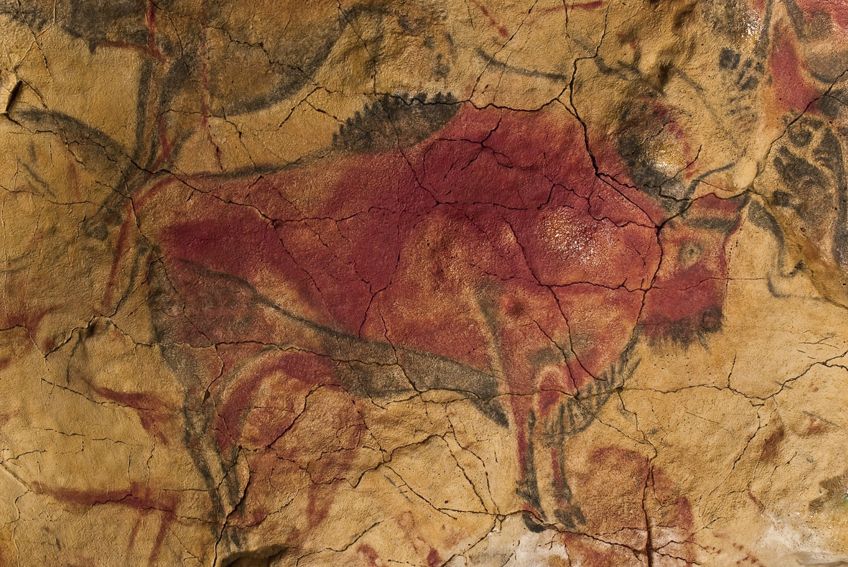
Some of the most common forms of Paleolithic art are paintings, and the vast majority of these are Paleolithic cave paintings. While there have been instances of paintings located in non-cave locales, the best-preserved are typically found in caves. This is because caves provide natural protection from the elements, and some of the most famous of these caves will be discussed below.

Paleolithic Architecture
In the Paleolithic era, the ability to construct permanent structures was generally beyond the ability of ancient people. Most of the structures that were built by early humans were made of wood, vegetation, and animal skin. These would have been particularly useful for nomadic people as they could be easily disassembled. Caves were far better for permanent homes though, but there have been indications of some structures made of stone from this era.
However, much of human architecture started in the later parts of the Stone Age with locations such as Gobekli Tepe in Turkey.
Paleolithic Sculptures
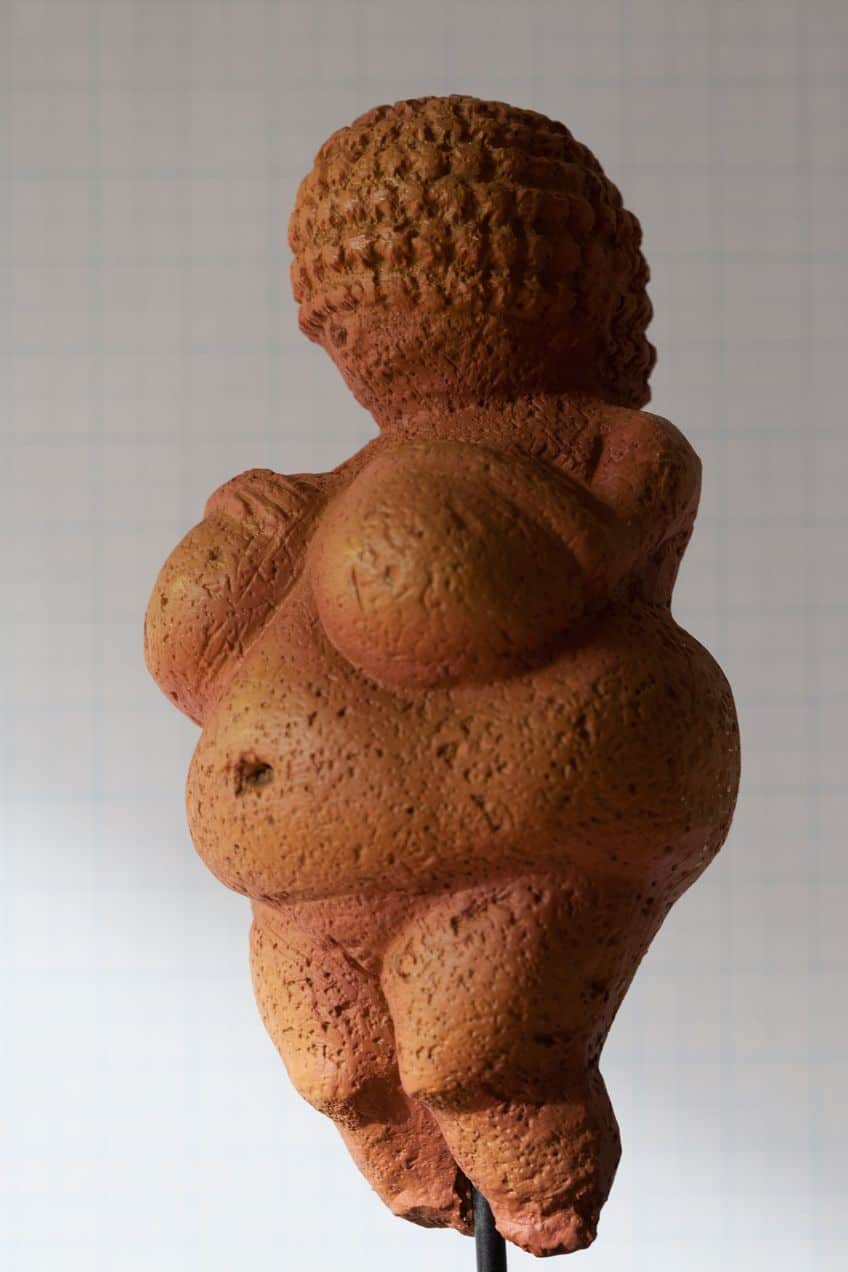
With the advent of stone tools during the Paleolithic period, the ability to carve things became possible. Sharpened tools could be used to carve stone, bone, or ivory, and there are also instances of ceramics that would have been made from clay. Some of the most common instances of Paleolithic sculptures include the Venus figurines, which are accentuated female figures that emphasize sexual characteristics.

Examples of Paleolithic Artworks
Let us have a look at a few specific pieces of Paleolithic art. Below, we will discuss five of the most famous of these ancient pieces of art, but it is first worth stating that the dates provided for each of these are a general estimate. Thanks to the immense age and lack of record-keeping from the Paleolithic period, we can only determine the dates to a general period. In the contemporary era, we can often tell when something was created to the date because we like keeping records, but Paleolithic people didn’t have written language yet.
In addition, it should be mentioned that interpretation of artworks is already a difficult thing because art is inherently subjective and what any one person believes a piece of art is about may be disputed by anyone else.
The same goes for Paleolithic art. However, the major difference is that we at least know the cultural origins of many pieces of art from the last few thousand years, but we do not know that as much when it comes to the Paleolithic period. We do not know what these artworks mean, but we can make educated assumptions about them. So, let’s get started.
Lion-man Sculpture (39,000 – 33,000 BCE) from Hohlenstein-Stadel
| Date | 39,000 – 33,000 BCE |
| Materials Used | Ivory |
| Function | Sculpture |
| Discovery Location | Hohlenstein-Stadel, Germany |
The Lion-man sculpture, also known as the Löwenmensch figurine, is an ancient ivory figure that is one of the oldest pieces of Paleolithic art that has ever been discovered. The German name is often used to describe this particular piece of ancient art because it was discovered in Germany.
This figurine stands at a height of 31.1 cm (or 12.2 in) and is an intricately carved figure that depicts a humanoid character with a lion’s head. This, aside from it being one of the oldest pieces of Paleolithic art in the world, also means that it is one of the oldest instances of zoomorphic art. The tradition of anthropomorphic images has persisted into the present day in human artworks.
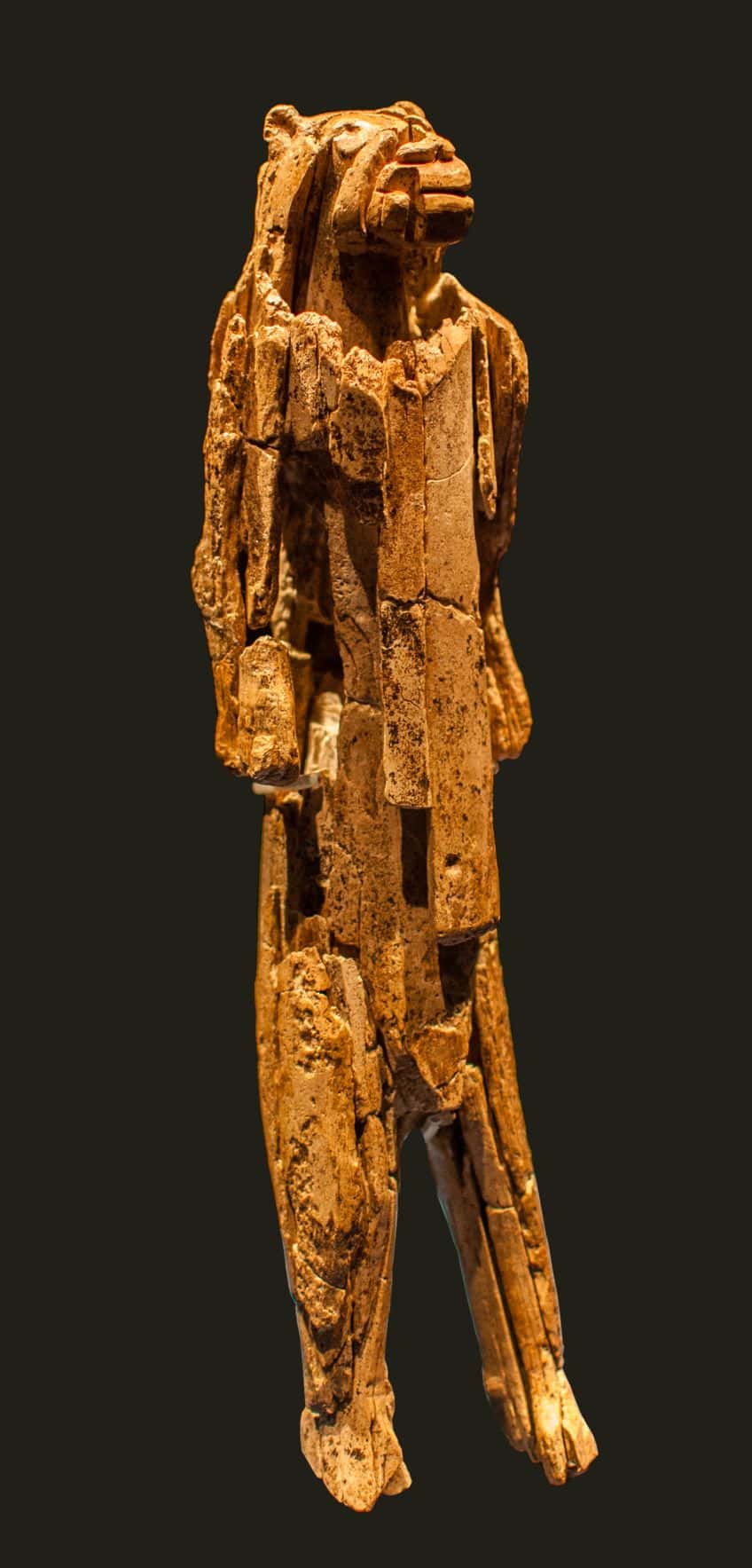

The Lion-man sculpture was carved from ivory, but thanks to the incredible age of this artwork, it was not carved from elephant ivory, but rather from a mammoth’s tusk. The detail on the design indicates that this would have been carved using a flint knife, and carving something like this during this time period would have taken considerable time and skill. Findings from the same cave network indicate that these ancient people possessed the knowledge to work with ivory of this description.
One of the elements of the Lion-man sculpture that has been discussed since it was discovered is the possible sexual characteristics of the figurine. It has been suggested that a plate on the abdomen may have indicated a penis design, but other elements may indicate that it was meant to be a female. There are still debates about the sex of this figurine, but it may not even be possible to determine this with any degree of certainty.
However, it is an interesting aspect of the design to discuss and contemplate.
Chauvet-Pont-d’Arc Cave Paintings (Possibly 35,000 – 31,000 BCE) from Ardèche
| Date | Possibly 35,000 – 31,000 BCE |
| Materials Used | Paint |
| Function | Cave paintings |
| Discovery Location | Ardèche, France |
The Chauvet-Pont-d’Arc Cave paintings are a series of Paleolithic cave paintings that were discovered in France, and there are actually a fairly large number of ancient sites discovered in France, and so you can expect more sites on this list to be from the country. In the case of this particular cave, it contains some of the best-preserved instances of figurative cave paintings that have ever been discovered.
This site was considered to be significant enough to understand the development of Paleolithic culture and the history of cave paintings that it was declared a UNESCO World Heritage Site. It has been extensively studied ever since it was discovered in 1994. While the Paleolithic cave paintings will be the primary focus here, it is also worth mentioning that the caves also led to a variety of other discoveries. The location contained a number of fossilized remains and even markings from animals, and some of those animals are extinct today.
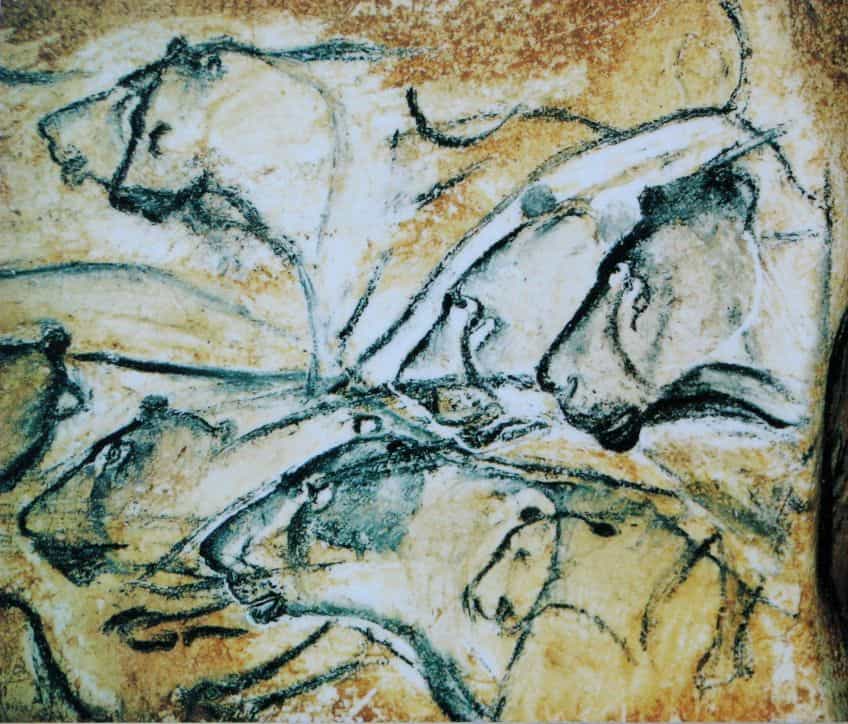

The caves contain hundreds of Paleolithic paintings along the rock walls, and these depict a variety of animals. Some of these animals have not been recorded elsewhere, but there are many that are known to us, such as mammoths, hyenas, and cave lions. Thirteen separate species have been identified in these paintings, and as is fairly common in much of Paleolithic art, there are no completely human figures.
It has been theorized that many ancient cultures believed in a form of animistic religion, and so the use of animal and natural forms may have been quite commonly used. However, there does appear to be one particular female figure, known as a Venus, but it may have been connected to a bison’s head to create a more minotaur-like image. Other than these images, there are also many abstract images that may indicate forms of spiritual and shamanistic practice. Lastly, the dating of this site is a somewhat difficult thing. There has been some level of dispute with the oldest suggested date being included in this particular list, but the period in which some of the paintings were created may have been several thousand years younger.
However, as there have been conflicting radiocarbon dating, it may also indicate different stages of inhabitation of the caves.
Venus of Dolní Věstonice (29,000 – 25,000 BCE) from Dolní Věstonice
| Date | 29,000 – 25,000 BCE |
| Materials Used | Ceramic |
| Function | Sculpture |
| Discovery Location | Dolní Věstonice, Czech Republic |
The Venus of Dolní Věstonice is a female figure that was created out of ceramic, and it is one of the oldest known forms of the Venus image. This particular Paleolithic sculpture depicts a naked female human that is designed in a more rounded shape with accentuated female characteristics. This particular Venus figurine is among the oldest known pieces of ceramic art in the entire world.
This ceramic Venus figurine was discovered in a Paleolithic site from which the figurine gets its name. This site is located in the Czech Republic, and the region around this ancient site contains some of the oldest instances of Paleolithic artwork that we have ever discovered. This particular figure is relatively small at a height of 111 mm (or 4.4 in) and a width of 43 mm (or 1.7 in).
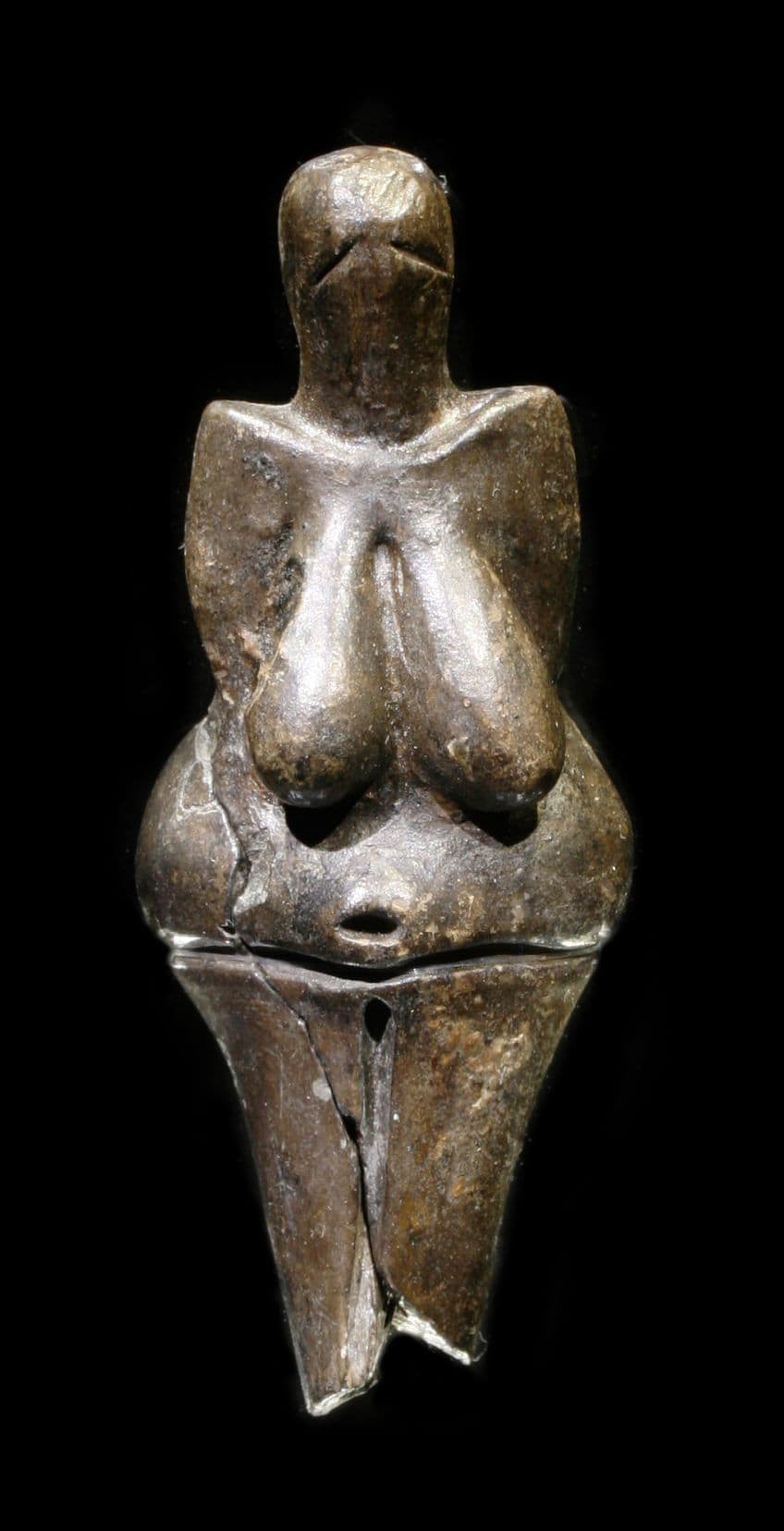

The ceramic Venus fits easily into someone’s hand, and the figure makes use of many of the accentuated features associated with Venus images. It includes large breasts, hips, and a belly with a relatively small head. These exaggerated features are those most associated with fertility, and as such, this image may have been carved as a symbol of fertility. However, with any Paleolithic artworks this ancient, we cannot be definitively certain about anything.
One of the unfortunate aspects of this particular figurine is that it appears to have broken at some point in its history. There are markings at the back of the Venus figure that appear to be holes for featured ornamentation. Daintier features such as this often do not manage to survive through the millennia and so it makes sense that if any part of the design breaks, it would be the structurally weakest aspect of it. This Venus figurine was also found alongside numerous other figurines, and many of them were animal in nature. There were bears, lions, mammoths, and many others.
The ancient humans that lived in this particular region appear to have been adept at Paleolithic pottery.
Cosquer Cave Paintings (25,000 – 17,000 BCE) from the Calanque de Morgiou
| Date | 25,000 – 17,000 BCE |
| Materials Used | Paint |
| Function | Cave paintings |
| Discovery Location | Calanque de Morgiou, France |
The Cosquer Cave paintings are a collection of Paleolithic images located in France. One of the most interesting things about this particular cave network is that the entrance to the cave is located about 37 m below the surface of the water. The caves would have been above the water level when they were originally used, but the sea level rose during the thousands of years between their use and their contemporary discovery.
This particular archaeological site was discovered by mistake by a number of divers in the early 1990s, and it was named after one of those who actually died after getting lost in the caves. Most of the Paleolithic artworks located in the cave were destroyed by seawater over the years, but there are about 500 of these Paleolithic cave paintings that have managed to survive.
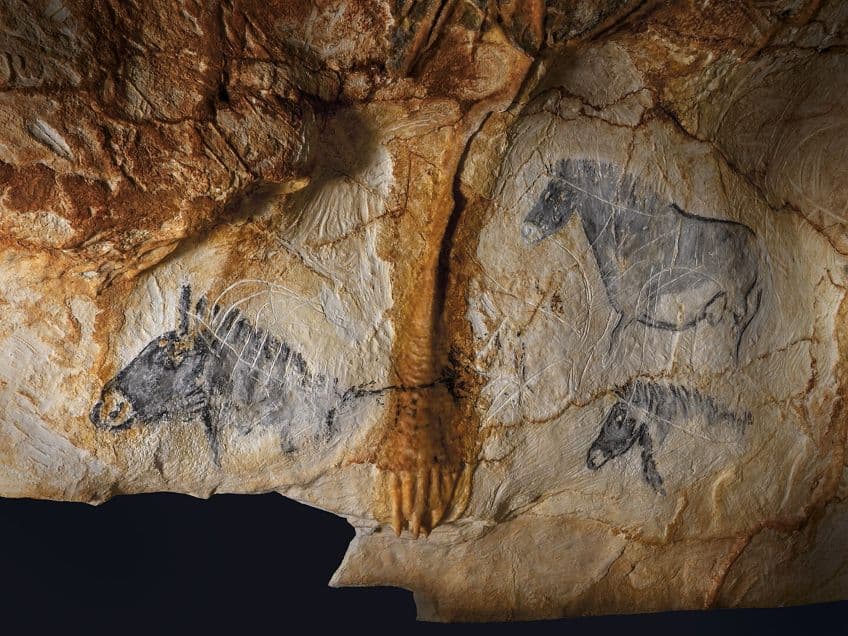

Many of these images include hand stencil paintings, animal images, and various marine animals. Marine animals are some of the more unusual images to have been discovered in Paleolithic art, but as this cave network would have been near the ocean, it does make sense that they would also be depicted. Additionally, the human images often contain exaggerated sexual components as is quite common in much of Paleolithic art.
The far more recent discovery of this cave network shows the way in which the history of cave paintings is not yet entirely known. There may be other caves in the world full of other instances of Paleolithic art that have yet to be discovered. Perhaps they will eventually be discovered, but we cannot know whether we will ever discover it all.
The world is full of mysteries, and the lateness of discoveries such as this only serves to reinforce that reality.
Lascaux Cave Paintings (15,000 BCE) from Dordogne
| Date | 15,000 BCE |
| Materials Used | Paint |
| Function | Cave paintings |
| Discovery Location | Dordogne, France |
The Lascaux Cave paintings come from a cave network located in France. This particular cave network is a large one that contains numerous Paleolithic cave paintings that cover the walls and ceilings of the cave network. As is common in much of Paleolithic art, these painted figures tend to be animal in nature, and there are over 600 of these paintings within these particular caves.
These Paleolithic paintings are made up of a total of nearly 6,000 figures spread over the course of the many paintings throughout the cave network, and the immense quantity of paintings means that these images would have been the work of numerous generations. There is still some debate about the age of these Paleolithic cave paintings, but the effort needed for their creation has never been debated.
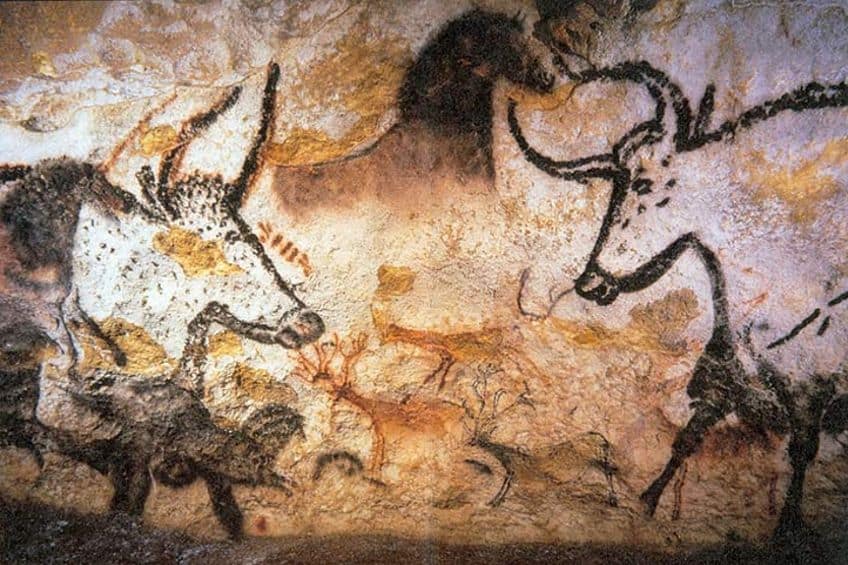

The site was also declared to be important enough to become a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 1979 because of the immense value in the cave network with regard to understanding Paleolithic culture and artistry. The figures are also painted using a variety of colors, such as red, yellow, and black, and indicated some ability to create different pigments. However, the site does not only include paintings, but also Paleolithic drawings that were carved into softer parts of the rock. Some of these images, alongside a number of the paintings, have faded with time. This is expected of such ancient sites, but the majority of the paintings have been remarkably well preserved.
The section of the cave that is typically considered to be the most famous is known as the Hall of the Bulls. This particular section is where many images of bulls, stags, and a bear are located. The largest of all these bull paintings is 5.2 m (or 17.1 ft) long. This makes it the largest such image ever discovered.
With that, we conclude our look at Paleolithic art. We have given a Paleolithic art definition, a brief history of the Paleolithic period, and various examples of Paleolithic artworks that are famous today. Hopefully, you have learned a good deal about these ancient pieces of human artistry, and while we cannot know much about these artworks other than that they exist, they do show us some of the oldest history of our people.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Does Paleolithic Mean?
This term is another name that refers to the human Stone Age. This particular period was an immensely long one and lasted for about 3.4 million years. The reason for the name of the Age is because this was the period during which humans managed to make use of stone tools. Many of the earliest aspects of human ingenuity arose during this period, and the stone age officially came to an end with the advent of human metalworking.
What Is Paleolithic Art?
This is a form of artwork that originates from the earlier portion of the human Stone Age. This period was marked by the human ability to make use of stone tools and as such, many of the most ancient pieces of human artwork made use of stone tools in their design. Paleolithic paintings and sculptures were particularly common during this period. However, the design of the various pieces of Paleolithic artworks was not particularly complex by today’s standards. So to sum it up, this is a Paleolithic art definition.
Are There Any Known Paleolithic Artists?
The Paleolithic culture and era was one that predated writing systems, and as a result, there is an understandable lack of record-keeping from the Paleolithic period. We have no idea who created any of these images or sculptures, and we do not know the cultures, religions, or beliefs of those who did. We can only make our best approximations based on what we can see.
What Is the Oldest Paleolithic Artwork?
The oldest known piece of Paleolithic art is likely the Lion-man figurine that was discovered in Germany. This sculpture is dated at around 40,000 years ago. It depicts a humanoid figure with a lion’s head, and it has also become one of the most famous pieces of Paleolithic art. The patience required to carve something of this description with the tools at the time is part of what has made it such an interesting artifact.
What Is the Most Famous Piece of Paleolithic Art?
Fame is a subjective metric, but some of the most famous pieces of Paleolithic art include the Paleolithic cave paintings in the Lascaux and Chauvet caves, and also the various Venus figurines that were carved during this long period of human history. There are many Paleolithic drawings and designs that have become synonymous with the period.
Liam Davis is an experienced art historian with demonstrated experience in the industry. After graduating from the Academy of Art History with a bachelor’s degree, Liam worked for many years as a copywriter for various art magazines and online art galleries. He also worked as an art curator for an art gallery in Illinois before working now as editor-in-chief for artfilemagazine.com. Liam’s passion is, aside from sculptures from the Roman and Greek periods, cave paintings, and neolithic art.
Learn more about Liam Davis and about us.
Cite this Article
Liam, Davis, “Paleolithic Art – Exploring the Early Art of Humanity.” artfilemagazine – Your Online Art Source. October 2, 2023. URL: https://artfilemagazine.com/paleolithic-art/
Davis, L. (2023, 2 October). Paleolithic Art – Exploring the Early Art of Humanity. artfilemagazine – Your Online Art Source. https://artfilemagazine.com/paleolithic-art/
Davis, Liam. “Paleolithic Art – Exploring the Early Art of Humanity.” artfilemagazine – Your Online Art Source, October 2, 2023. https://artfilemagazine.com/paleolithic-art/.