What Is Drawing? – Learn a Wide Range of Techniques to Drawing
Drawings are arguably the most widely established forms of visual art. Requiring very little to get started, drawing is often the first art form that many will explore. However, have you ever considered what is drawing exactly? Below, we will have a look at the history of drawing, as well as how an artist can create awe-inspiring pieces by simply using lines on a two-dimensional surface.
What Is Drawing?
Historically, drawing has had many uses from providing informational illustrations to expressing creativity. Today the wide range of techniques, tools, and technologies means you might struggle to find a single drawing definition. The line distinguishing a drawing from a painting has also become blurred as artists have begun mixing different media and mediums. A drawing definition can be created in terms of the types of materials that the artist has used. Traditional drawing mediums are usually dry mediums such as graphite, charcoal, pencil, pastel, chalk, and even metals.
However, some mediums such as ink are used to create drawings as well as paintings. Therefore, in this article, we have distinguished drawings from paintings by the way that the materials are applied.
Materials applied using a pen, crayon, stylus, or similar tools then the artwork can be considered a drawing. If the piece has been made using your usual painting tools like brushes, painting knives, or sponges then it can be considered a painting. Drawings are done on two-dimensional surfaces, such as paper, canvas, wood, or even leather, and are done using lines, marks, and regions of tone. These lines are a crucial part of drawings and distinguish them from paintings, which focus more on texture and brushstrokes. While this is our drawing definition, there are many other possible interpretations.
The History of Drawing
Over 30,000 years ago the first drawings appeared in caves. These drawings were created by early humans using the ash from burnt sticks or red ochre and included depictions of animals and simple human figures. The earliest instance of human drawings was a cross-hatched pattern drawing using an ochre crayon found in South Africa, which dates to the Stone Age. Despite this, it was not until the Renaissance of the 14th century that drawing became a medium in itself, and not merely a planning tool.
The Evolution of Drawing
In the past, drawings were largely monochrome or had very little color, because of the materials that these artists used. Today drawings can be made with vibrant colors, using colored pencils or pastels, that rival that of paintings, and even on graphic tablets. Some drawing mediums even mimic painting mediums such as watercolor pencils, which are applied dry like ordinary colored pencils but produce a watercolor effect when moistened with water. Traditionally, drawings were used in the planning and preparation of artworks in other mediums. Pencil sketches were used, and are still used today, early in the artistic process.
Drawing and sketching allows artists to plan out the spacing, composition, and perspective of their piece. This means that artists from all mediums from painters to sculptors, and even digital artists use drawing as an integral part of their work.
Drawing is therefore not only a fundamental skill for all artists but also forms the basis of visual arts. The immediacy in which a drawing could be made compared to other mediums also allowed artists to capture ideas and scenes in the moment. These drawings could then be used to create pieces in more gradual mediums such as paintings and sculptures. Aside from being used to brainstorm and explore other techniques and mediums, drawings were also done to communicate information and ideas. Drawings can convey many forms of information in a way that surpasses language barriers such as instructions, scientific journals, historical events, or even simply as entertainment or artistic expression.
Famous Drawers and Drawings in History
Arguably the most recognized drawing artwork in history is The Vitruvian Man (1490) by Leonardo da Vinci. This work was indicative of the mixture between science and art of the Renaissance era, as well as the prominent role that drawing played in critical thinking and problem-solving. Da Vinci had notebooks filled with detailed drawings and sketches of inventions, plants, and even human and animal anatomy. Another famous drawing is Knight, Death, and Devil (1513) by Albrecht Dürer. Dürer produced many woodcuts, engravings, and etchings, which were all based on the heavily detailed drawings that he created. He revolutionized printmaking into a recognized art form and inspired many artists to make and distribute their own prints.
Rembrandt is an artist known for his versatility in media and subject matter.
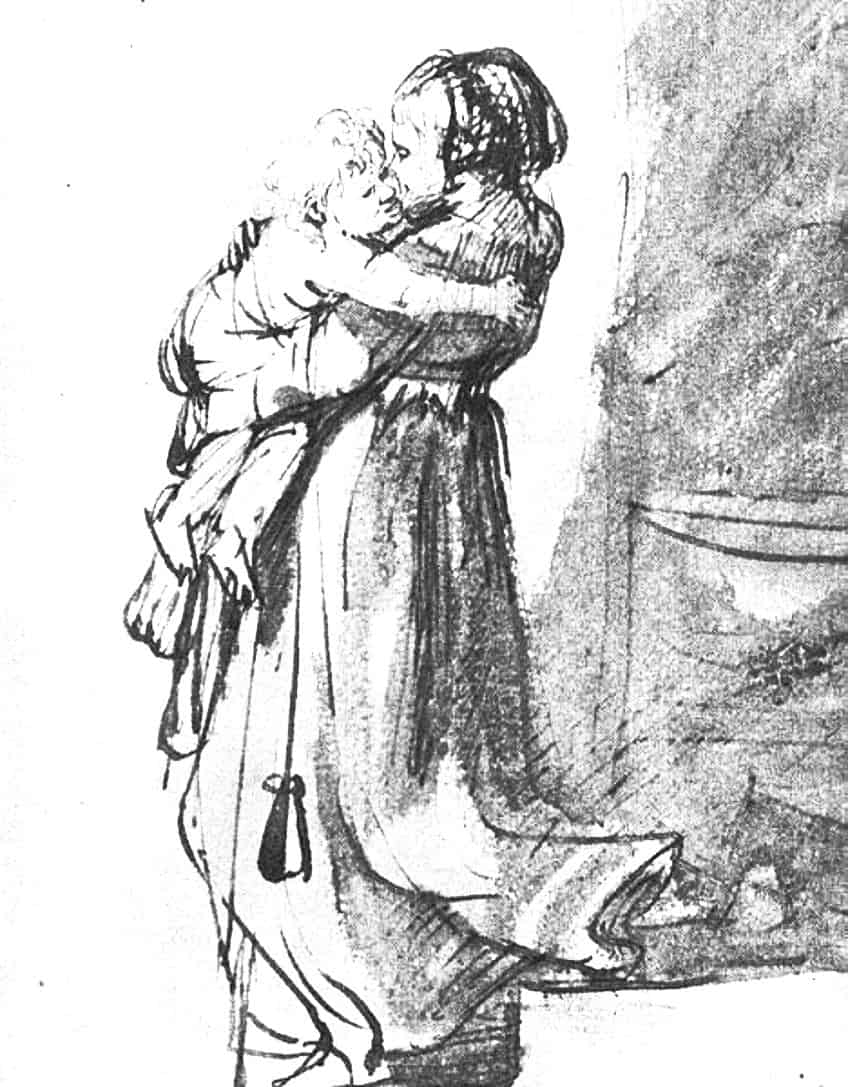

This remains true for drawing mediums, which the artist used to capture different subjects and landscapes swiftly and with confidence. The well-known ink drawing Woman Carrying a Child Downstairs (1636) highlights Rembrandt’s artistic skill in the art form. Edgar Degas is an impressionist artist famous for his pieces depicting dancers and other human subjects in motion. In addition to his paintings, Edgar Degas produced many different drawings and studies of his subjects in pastels and pencil. The pencil Study of a Dancer in Tights (1879) is a superb example of how Degas used drawings to plan and achieve the movement found in his pieces.
Basics Tools and Materials for Drawing
Unlike other art forms, drawing requires very little tools and materials to get started, making it an obvious first choice for many new artists. Beginner artists can start simple with basic pencil and printer paper to practice their techniques, before investing in better drawing tools and paper.
Drawing Mediums
Artists can use many different mediums to draw with including pencils, charcoal, pen or ink, chalk, markers, colored pencils, pastels, silverpoint, and even crayons. Each medium offers its own benefits and style, so it can be helpful to try a few out to see which are right for you and your drawing style.
Pencil
Pencils are a graphite-based drawing medium which comes in a variety of hardness’s for different drawing needs. B-grade pencils are softer and great for blending and smudging, while H-grade pencils are harder and better suited for sketching or technical drawings.
Colored Pencil
Colored pencils are a newer drawing medium and only became widely used at the beginning of the 20th century. Unlike regular pencils, they do not contain any graphite but are made from an oil- or wax-based core that contains colored pigments. Watercolor pencils contain a water-soluble binder in place of wax, which gives them added versatility but reduced pigmentation.
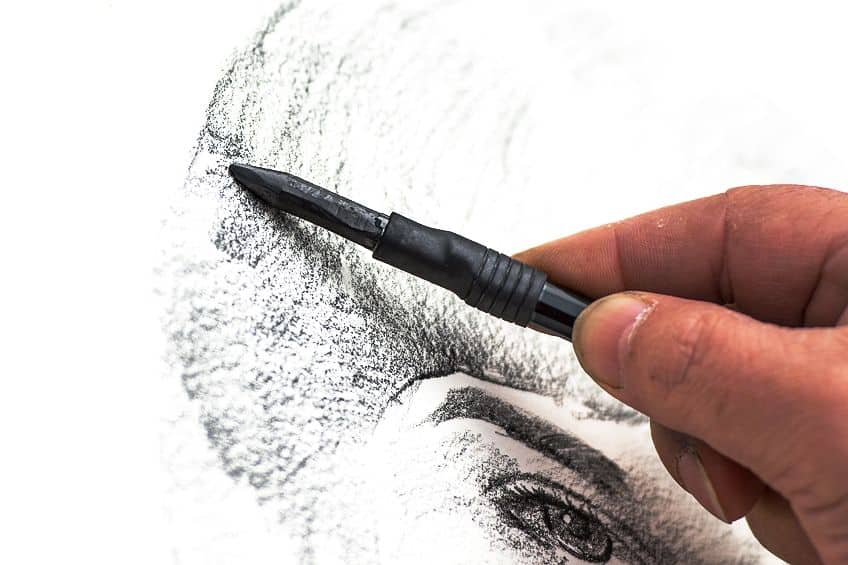
Charcoal
Charcoal is a very old drawing medium, seen on cave walls as far back as 30,000 years ago. This medium is created by combining powdered organic material with a wax or gum binder and comes in both thick and thin varieties. Charcoal is easy to smudge and erase, so it requires a fixative to ensure its longevity.
Ink
Ink has been used in many ways to create art. Ink pens and markers are great for drawings, illustrations, and calligraphy and come in many different colors, finishes, and opacities. Ink can also be used alongside many other drawing mediums to add some bold contrast.
Pastel
Pastels are a versatile and vibrant drawing medium that has been used since the 18th century. Pastels come in two broad varieties, namely water pastels and oil pastels, as well as many different consistencies for smudging or creating hard lines. Like charcoal, pastel drawings require fixatives to ensure their longevity.
Metalpoint
Metalpoint is a drawing medium that typically involves using a thin stylus of either silver or lead. While silverpoint and leadpoint are the most common metals used, gold, copper, bronze, tin, platinum, and brass have also been used to create drawings using this technique in the past.
Drawing Tools
Aside from your medium of choice, you will need a few other tools to create your drawings. Some basic drawing tools include an eraser, sharpener, smudging tool, blotting paper if you are using ink, drafting or painter’s tape to secure your paper, and a table, easel, or drawing board to support your drawings. A ruler, circle compass, and set square are also very helpful tools to have on hand when drawing artwork.
Paper
The paper you use for your drawings is a very important decision. Different paper types have different qualities and are better for using with some mediums over others. Paper types vary in acidity, hue, texture, and strength. Regular printing paper is inexpensive and can be used for practicing techniques or rough sketches. Tracing paper is thin and translucent and can be used to transfer drawings or experiment over them. Smoother papers are great for more detailed drawings, while rougher or toothier papers are better for creating deeper contrast.
Bristol board, and other heavy acid-free boards with smooth finishes, can be used for drawings with fine details as well as more wet mediums as they do not distort when wet.
Vellum is an exceptionally smooth paper and can also be used for drawings with fine and intricate details. Cold-pressed watercolor paper can be used with watercolor pencils or other wet drawing mediums such as ink. Linen paper, parchment paper, and canvas have rougher surfaces and can be used with charcoal and pastels for more vibrant drawings.
Basic Techniques for Drawing
Drawing may be one of the easiest art mediums to start with, but it still requires a lot of time and practice to perfect. Understanding line, shape, form, and perspective in drawing is very important and there are many techniques you can use when drawing artwork to hone these skills. Through the use of proper techniques, you can achieve the same amount of depth, color, and realism as paintings.
Shading Techniques
The most important drawing techniques to learn are shading techniques. Shading is the process of adding various tonal values to your drawing to represent the placement of light and shadows on your subject. Shading brings depth, weight, and contrast to your drawings when used correctly by creating areas of light and darkness within the subject. Shading includes a variety of hatching and stippling techniques to produce the desired effect.
An artist may also leave sections of their drawing untouched or protected with tape or masking fluid to preserve lighter areas and highlights.
Parallel-Hatching
Parallel-hatching, or just hatching, is the most common drawing shading technique. This method involves making small, parallel ticks on your paper. Hatches that are closer together create darker areas and can be used for shading in drawings. Hatches that are further apart can be used to add texture to the area instead.
Cross-Hatching
Cross-hatching technique is similar to parallel hatching, only it uses a series of small ticks that intersect each other in a cross-like pattern, instead of lying parallel. This technique adds more darkness and depth to the area than is possible with parallel-hatching. The closeness of the perpendicular ticks can be varied to increase or decrease the shadow, with closer lines creating darker areas and further apart lines creating lighter areas.
Contour-Hatching
With the contour-hatching technique, the hatch marks follow along the curves and contours of the subject. This method also adds shading and value to the drawing but creates a greater sense of volume than other hatching methods. Contour hatching also gives drawings a more three-dimensional look and feel.
Stippling
The stippling drawing technique uses small dots instead of ticks to create shading. In this method, numerous tiny dots are added to an area to increase the shadows in that section of the subject. Dots that are closer together will produce areas of darker shading than dots that are further apart.
Other Drawing Techniques
There are many other useful drawing techniques aside from shading that can be used to create a variety of effects in your piece. Below, we explore some of the most popular drawing techniques used by different mediums throughout the drawing process.
Tracing
Tracing is a technique that involves transferring a drawing from one surface to another by creating a copy. There are many methods to trace a drawing, however, the most popular tracing technique is using tracing paper to outline the drawing.
Burnishing
Burnishing is a technique often used with colored pencils to intensify the color. Burnishing involves adding colors in layers or using a solvent to cover all of the paper underneath. This technique gives colored pencils a similar look and opacity to paints.
Blending
Blending involves softening or spreading the drawing strokes that make up your piece, giving them a softer look or a more gradual transition. Blending is a technique that works best on mediums that are prone to smudging such as charcoal, graphite, chalk, or even wet ink. You can make use of many tools to blend your drawings including a blending stump, smudging tool, tissue, chamois, eraser, or even your fingers.
Be sure to test each method out with your chosen medium before using it in your drawings.
Subtractive Drawing
Subtractive drawing is another drawing technique. In this technique, the drawing surface or paper is covered with an erasable medium such as graphite or charcoal. Parts of the medium are then erased to create the outline of your drawing making use of negative space to create the image.
Armature Drawing
Keyline or armature is a great drawing technique, particularly for those starting out with figure drawings. This technique involves drawing the position of the figure’s limbs and body using simple lines and shapes. This creates a skeleton of sorts on which to build your drawing on. Armature drawing teaches you figure proportions and how to create poses in your drawings.
Line Drawing
Line drawings make use of simple lines to depict the subject. This is usually done in the absence of shading, blending, and color gradients to truly highlight the lines themselves. Most sketches are considered line drawings; however, they can also be completed pieces. Many artists challenge themselves to draw a subject using a singular, unbroken line that is created without lifting their drawing tool from the page.
Different Types of Drawing
There are many different types of drawings and many ways to classify them. The three most popular ways of categorizing drawings is by how representational it is, the medium being used, or the subject of the drawing. The distinction between these categories is not always distinct and drawings can incorporate any combination of these characteristics.
Representation-Based Drawing Types
The first way of categorizing drawings is based on how representational the drawing is of its subject. Drawings can be more life-like or more abstract depending on the art style, technique, and vision of the artist. There are three categories of representation types, namely realistic, symbolic, and expressive drawing types.
Realistic Drawing
Realistic drawings aim to accurately represent the subject within the illustration. They aim to translate the three-dimensional world around us onto the two-dimensional drawing surface by matching color, shape, value, space, texture, and any other aspect of the subject. This type of drawing is often the first type that students are taught and is important for learning how to reproduce your surroundings onto the page.
Symbolic Drawing
Symbolic drawings use shapes, lines, and marks to represent subjects that are larger or more complex. These types of drawings are generally simplified forms of an object; however, the object still remains recognizable. You can even create your own symbols and use them within your drawing.
Expressive Drawing
Expressive drawings are the most abstract drawing type. These drawings are often used to represent ideas, emotions, memories, spirituality, or other intangible concepts. The marks and lines used to create these drawings are often very expressive, instilling these drawings with a sense of movement and energy.
Medium-Based Drawing Types
Another popular method of categorizing drawing types is through the medium that is used. As discussed earlier, drawings can be created using a wide variety of mediums. Each of these mediums brings a different quality and effect to your drawings and can either be used alone or in conjunction with other media.
Sketch Drawings
Sketches are rough, quick, and unrefined drawings that are created using freehand drawing. Sketches are usually not considered finished works; however, they serve a number of important purposes in the creative process. It can be used to rapidly capture or record something that interests an artist, it can be used to develop or explore an idea, it can form the basic structure that the final drawing artwork is built upon, or it can be used to quickly represent an idea or image graphically.
While a sketch can be done in any medium, the most common medium to use is pencil. Less commonly, sketches can be done in wet mediums such as paint, or in three-dimensional shapes using clay.
Charcoal Drawing
In charcoal drawings, charcoal sticks are used to produce various black and gray linear effects. By changing the angle of the stick, as well as the pressure applied, you can create a multitude of line thicknesses and textures. Charcoal is also easy to manipulate using your fingers or a smudging tool, making it great for blending and creating shadows. However, due to the smudging characteristics of charcoal, a fixative or sealant must be applied to the final piece to preserve the drawing.
Pen and Ink Drawing
Ink comes in many forms from ink pens to markers and even pots of ink. Ink drawings have bold lines, usually with clean and defined edges. Traditionally, ink drawings are done in black or brown ink, however, today there are a wide variety of colors and finishes including metallic and gloss. Ink can take some practice to use effectively, as it is a very unforgiving medium and mistakes are hard to conceal.
Ink is very versatile and can be used alongside many other drawing and painting mediums to create striking pieces.
Pencil Drawing
Pencil drawings are usually the first drawing type that artists explore. Pencils are widely available and budget-friendly and therefore make for the perfect beginner drawing medium. There are many grades of pencils from soft pencils on the B side to harder pencils on the H side. B-grade pencils are mostly used for drawing as the soft nib allows you to shade and smudge more easily compared to H-grade pencils which are mainly used for sketching.
Colored Pencil Drawing
Using colored pencils, you can create colorful, rich, and vibrant drawings that rival paintings. Like graphite pencils, colored pencils are widely available and budget-friendly. These pencils come in both wax and oil varieties, which can produce smooth and pigmented drawings. The fine details that can be achieved with colored pencils means that these drawings can be more abstract or photorealistic.
Pastel Drawing
Pastel drawings can look strikingly similar to paintings; however, they are clearly distinguished by the linear markings made using pastel sticks. Pastels produce drawings that are smooth and rich in color and are best used on rougher drawing surfaces. In pastel drawings, the entire drawing surface is not covered in pastel. Instead, the drawing surface or paper is allowed to show through.
Pastels make use of some painting techniques, such as layering; however, this medium is applied dry like charcoal.
Subject-Based Drawing Types
The third most popular way of classifying drawing types is by the subject that is depicted in the piece. There are a few broad categories of subjects including figures, landscapes, still-life, and non-objective subjects. Below, we discuss some of the most popular subjects depicted in drawings.
Figure Drawing
Figure drawings are drawings that capture the human form. These drawings can include a variety of art styles and poses, from cartooning to photorealistic depictions. Figure drawings can include human anatomy as well or only sections of the human body. Portraiture drawings, which focus on the human face and expressions, are also included in figure drawings.
Landscape Drawing
Landscape drawings capture the environment around you. They can include the natural environment, cityscapes, or even seascapes. Landscape drawings require artists to have good observational skills to be able to translate the three-dimensional environment into the drawing surface.
Non-Objective Drawing
Also known as abstractions, non-objective drawings are abstract in nature, and do not depict any specific subject. These drawings tend to include simple shapes and geometric patterns, and usually aim to convey an idea or emotion rather than a subject.
The Benefits of Drawing
Drawings offer a multitude of benefits to artists aside from producing an artistic piece. Drawing works to improve your hand-eye coordination. Physically using a pencil as well as replicating subjects on canvas improves your ability to coordinate hands and eyes and is a vital skill in everyday life. Another benefit is improved memory, as when you draw something your mind is forced to process your subject in all its dimensions, such as visually, kinesthetically, and semantically. The finer details and characteristics you would usually dismiss are brought into focus when drawing a subject. This usually means you will remember those details when working on a scene later or passively become more aware of details in your everyday life.
Aside from the mechanical uses, drawing with its unique capacity for speed and spontaneity, also exercises the creative dimensions of the brain.
Creativity is made up of a combination of memories and experiences and uses many parts of the brain in unison. With practice, drawing results in these pathways becoming faster and more connected. Drawing can also be a relaxing, meditative, and absorbing experience, as well as serve as a creative outlet that increases dopamine levels through a variety of forms. Keeping visual diaries documenting your feelings are good for later reflection and can be richly rewarding practices.
Drawing has been defined in many ways since the Stone Age. Since its emergence as an art form in the early Renaissance, drawing has provided artists with a quick and readily-available tool for planning, relaying information, and artistic expression. The wide variety of drawing techniques, tools, and mediums make it a versatile art form for beginners and professionals alike.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is Drawing?
A drawing is an artwork made using materials that are applied to a two-dimensional surface using tools such as a pen, crayon, or stylus. Drawings are often made using dry mediums such as pencil, charcoal, or pastel, but can also be made with wet mediums like ink.
What Are the Benefits of Drawing?
Drawing offers many benefits including improved creativity, hand-eye coordination, and memory. Drawing has also been shown to reduce stress and promote mindfulness.
Liam Davis is an experienced art historian with demonstrated experience in the industry. After graduating from the Academy of Art History with a bachelor’s degree, Liam worked for many years as a copywriter for various art magazines and online art galleries. He also worked as an art curator for an art gallery in Illinois before working now as editor-in-chief for artfilemagazine.com. Liam’s passion is, aside from sculptures from the Roman and Greek periods, cave paintings, and neolithic art.
Learn more about Liam Davis and about us.
Cite this Article
Liam, Davis, “What Is Drawing? – Learn a Wide Range of Techniques to Drawing.” artfilemagazine – Your Online Art Source. July 17, 2023. URL: https://artfilemagazine.com/what-is-drawing/
Davis, L. (2023, 17 July). What Is Drawing? – Learn a Wide Range of Techniques to Drawing. artfilemagazine – Your Online Art Source. https://artfilemagazine.com/what-is-drawing/
Davis, Liam. “What Is Drawing? – Learn a Wide Range of Techniques to Drawing.” artfilemagazine – Your Online Art Source, July 17, 2023. https://artfilemagazine.com/what-is-drawing/.