What Is New Media Art? – How Modern Technology Influences Art
New media is a relatively misunderstood genre of art that many struggle to distinguish from digital art. So, what is new media art? In this article, we will dive into the history and development of this type of art by exploring the different characteristics of new media art, as well as a few influential figures of new media art who have drastically changed the way we view art and its relationship to media. Keep reading for all you need to learn about new media art!
What Is New Media Art?
The key term for understanding new media art in the 21st century is electronic media technologies and their function in creating, viewing, and engaging with art. What is new media art? New media art is a relatively recent term ascribed to artwork that is created using electronic technologies. These include digital art, computer graphics, animation, cyborg art, sound art, interactive art, video games, 3D sculptures made via 3D printing, internet art, and robotics. Such technologies are vastly different from that of traditional mediums found in visual art and architecture and were firmly rooted in the fields of performance, science, and art. In the Contemporary era, there has been a vast increase in the number of artists incorporating new media and electronic technologies into their artwork, such that new media artworks produced many unique experiences for art audiences of all ages.

With the gradual adoption of new media as a tool to enhance an audience’s engagement with art, new media art has tackled a variety of themes related to social and political activism, identity, Afrofuturism, databases, and feminism, which has helped grant new perspectives on complex themes. New media art is, therefore, at the heart of Contemporary art as a broad genre that encompasses engagements between the public and performative artworks, as well as social exchange and an opportunity to explore innovative technologies. As such, many tertiary institutions offer the opportunity for students to learn new media across the globe to propel the genre’s adoption by future generations.
It is also important to understand that new media art can include a variety of mediums, including traditional elements that form part of the new media experience.
As such, the common nodes among new media artwork share the elements of social participation and an exchange of some sort that ground the new media work. The creation of new media art also involves the curation and preservation of such experiences that are presented to the public in ways that are often more challenging than presenting traditional media. Today, it is almost considered the best or smart practice for most art institutions and museums to cater to exhibiting new media works and provide room for artists to offer new experiences with emerging technologies.
Tracing the Evolution of New Media Art
Now that you have an idea of what new media art is, you can now appreciate an in-depth review of the history of new media. When did new media art emerge, and who are the early pioneers of new media art? Below, we will discuss the history of new media art with new media art examples along the way for your benefit!

The History of New Media Art
So, when did new media art originate? New media art is believed to have originated alongside the development of what humanity can consider “new technologies” such as the phenakistoscope, which dates back as early as 1833. The concept of the moving image is the very conception of new media art, which was also marked by the invention of the praxinoscope in 1877 and later, the zoopraxiscope in 1879. Since then, new media was largely shaped in the early 20th century through the development of light art and kinetics in visual art. New media art examples from this period include Lumia (1919) by Thomas Wilfred and Homage to New York (1960) by Jean Tinguily, the latter of which was a self-destructing artwork.
Homage to New York by Jean Tinguily has been described as the early precursor of now fully modern new media artworks.
The artwork fused performance with kinetic artwork and was constructed using mechanical parts, including a piano, bicycle wheels, a radio, a toilet, a bassinet, and an American flag, all of which were coated in white paint. The new media artwork was exhibited in 1960 at the Museum of Modern Art and was divided into sections performed at different times. The performance’s climax resulted in the artwork destroying itself. The artwork was described as “a spectacle of abundance”.

Another notable movement was Futurism, which was credited as being the original site where performance and technology began to take shape. A few artists who experimented with then-new media included the choreographer, Valentine de Saint-Point and modern dancer, Loïe Fuller. New media and performance were also quite evident in early 1920s cabaret acts that included film projections in their performances, thus marking the dawn of new media in European culture. It is also important to recognize that new media is always changing as new technologies and innovations continue to shape the tools and mediums through which we create and present art. As such, the preservation of previous “new media” is essential to trace the history of new media art and its impact on how certain themes in art have been presented.
Early Pioneers and Developments in New Media Art
Among the most impactful new media artworks of the 20th century included Broadcast (1959) by Robert Rauschenberg in an interactive installation with three re-tunable radios and one painting. German sculptor and painter Wolf Vostell incorporated television sets in his new media art installation called TV De-collages, which placed the television set as the transmitter of media itself, which expanded the appeal of new media into almost every household.
New media art was therefore dubbed experimental art that incorporated new forms of media as the medium through which artists could discuss themes of identity and social politics amid computer technology.
Many artists from The School of the Art Institute of Chicago in the 1970s also pooled together to experiment with graphic design, installation, and sculpture, while establishing the Video Data Bank in 1976 for video art distribution. A project called Venus in Time was also undertaken by Donna Cox, George Francis, and Ray Idaszak, who combined their skills in mathematics, art, and computer science to transform mathematical data into three-dimensional sculptures, which also resembled the Paleolithic Venus figurines.
Another prominent development in new media art was also the PHSCologram, which was created in 1982 by Ellen Sandor and the specialists of a collective called (art)n Laboratory, who produced a visualization of the AIDS virus. This image was first used as the cover for the 1988 IEEE Computer Graphics and Applications. A year later, experts at the University of Illinois collaborated on a project called CAVE, which was a virtual reality immersion technology that utilized rear projection. Developments in biotechnology have also enabled artists to explore alternative mediums such as genetic codes and human DNA as artistic mediums.

One cannot discuss new media art without recognizing the role of the internet and the web in promoting new methods for new media artists to use. The concept of distributed authorship was pioneered by Roy Ascott in 1983 for his global telematic project, which debuted at the Musée d’Art Moderne de la Ville de Paris. Throughout the 1980s and 1990s, many artists leveraged the web, internet, and real-time technologies to produce many interactive new media artworks, including figures such as Vuk Ćosić, Ken Feingold, David Rokeby, Monika Fleischmann, and Michael Bielický. Subsequently, the first internet-based video archive for new media art was co-produced by the Centre pour l’Image Contemporaine, the Museum Ludwig, and the Centre Georges Pompidou.
The Characteristics of New Media Art
New media art has been influenced by many theories over the last century, including those surrounding themes of networks, hypertext, interaction, and databases. Prominent theorists include Theodor Nelson, Vannevar Bush, Italo Calvino, Jorge Luis Borges, and Julio Cortázar, whose literary works you might find appealing should you wish to explore the depths of new media art theory. What then are the characteristics of new media artworks? It has been proposed that new media artworks rely on fields that converge at three distinct systems: the art system, industrial and scientific research, and political-cultural media activism. New media art also aims to address Contemporary topics such as hacktivism, open-sourcing, computer art, identity, telepresence, collaboration, surveillance, appropriation, interventions, and corporate parodies.
One of the primary characteristics of new media art is its tendency toward non-linearity in interactive and immersive artworks.
Contemporary new media works also rely on the user’s interaction and experience with the artwork, such that it broadened the traditional perspectives of how one ought to experience linear interpretation and engagement. Non-linear new media artworks require the participation of the audience, where the visitor is accounted for in the artwork’s representation and thus informs the content displayed. Happenings (c. 1950s) by Allan Kaprow greatly influenced the elements of audience participation for many new media artists whose works were built on interactivity. Interactivity and the cross-connections spurred by the web and the internet have become useful tools for new media artists to explore themes of governmental, public, and corporate interest. New media art also integrates the primary use of digital tools and technologies, which allows artists to adopt a transdisciplinary approach to the concepts they represent. Since technology is so deeply rooted in almost every aspect of culture in the 21st century, its associations with other fields of interest are worth exploring to highlight the reach of new media.
Exploring Different Forms of New Media Art
The characteristics of new media art converge on art and its relationship to technology, as well as its impact on the experience and reception of art. Below, we will examine the different forms of new media art that have dominated the 21st century.
- Digital installations involve the use of interactive technologies that stimulate audience participation while drawing one’s attention to one or more elements of an artwork. Digital installation may feature a range of technologies such as three-dimensional images and video art to enhance the sensory experience beyond the visual experience.
- Virtual reality (VR) art in new media artworks provides experiences that are exhibited through stereoscopic displays or computer screens. Virtual reality art presents a simulated environment or scene, where artwork is presented and further information is provided via sound for a full experience.
- Augmented reality (AR) art can be used to create 3D sculptures and is used by many artists today to recreate public spaces and new landscapes. What makes augmented reality so special is that it can be used to stimulate interactivity using traditional mediums or produce new works in a digital environment.
- Video and media art encompasses art that relies on video recordings, projections, and films as a form of expression. This type of new media art is site-specific and can be viewed in different locations. Video and media art can be incorporated into installations and performances to enhance the experience of art.
- Internet art is another popular new media art form that relies on the “net” or internet as its primary medium. Such artworks were produced in the 1990s and early 2000s, when the internet was used to distribute art, which also challenged the idea of traditional institutions such as galleries and art museums, as the primary site for interacting with art.
Influential New Media Artists and Their Works
Since the 1960s, there have been numerous new media artists who have contributed to the popularity of the genre and its relationships with performance, social critique, and technology. Below, we have provided a selection of new media artists and their unique new media art examples that will give you a holistic understanding of what new media art is.

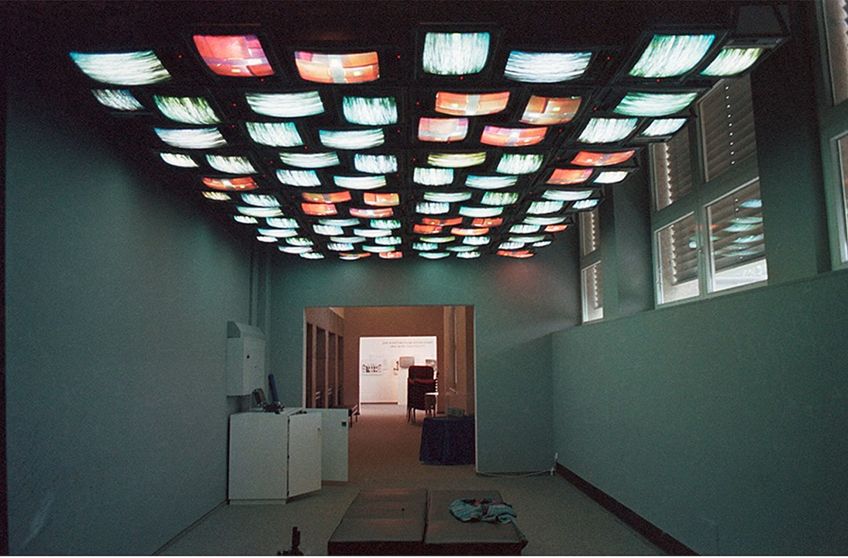
Nam June Paik (1932 – 2006)
| Artist Name | Nam June Paik |
| Date of Birth | 20 July 1932 |
| Date of Death | 29 January 2006 |
| Nationality | Korean-American |
| Associated Movements, Themes, and Styles | Modern art, Fluxus, Contemporary art, and new media art |
| Mediums | Installation, sculpture, video art, and technology-based art |
Nam June Paik was one of the most famous new media artists of the 20th century, whose experimentation with various media resulted in the invention of the term “electronic superhighway” in 1974.
Nam June was inspired by the 1950s and 1960s socio-political landscape of America, which he used to unpack ideas about the transference of information via light paths that could be accessed at any point in time or place.
His work on Electronic Superhighway: Continental U.S., Alaska, Hawaii in 1995 was a seminal video installation artwork that showcased the neon-lit highways of the United States, presented at the mode for electronic communication. Today, it remains an iconic work of new media art and the Fluxus movement.

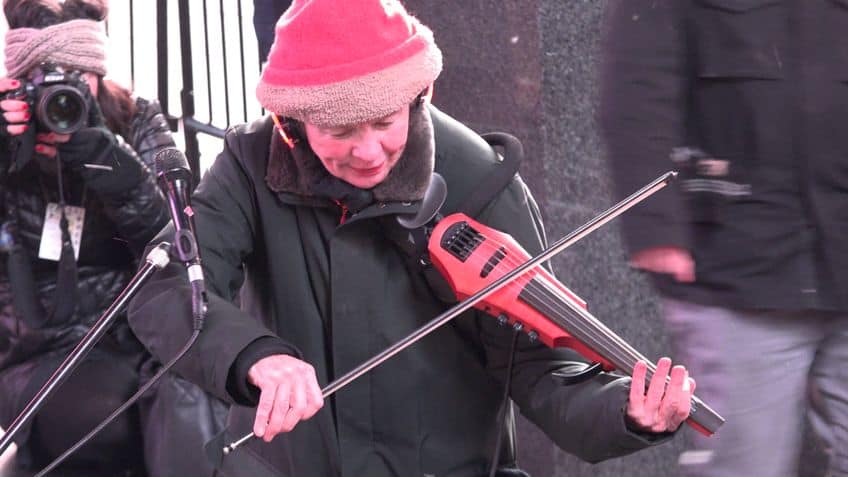
Laurie Anderson (1947 – Present)
| Artist Name | Laura Phillips “Laurie” Anderson |
| Date of Birth | 5 June 1947 |
| Nationality | American |
| Associated Movements, Themes, and Styles | Avant-Garde art, Contemporary art, and new media art |
| Mediums | Performance, music, writing, and filmmaking |
Multimedia artist Laurie Anderson is one of the most iconic new media artists of the 21st century, whose expertise in filmmaking, performance art, and music has provided some of the best multimedia experiences. Anderson is renowned for her invention of the tape-bow violin, which enables the use of a magnetic tape and tape recorder attached to a violin body.
The tool remixes the pre-recordings of the tape and distorts human speech over the playback, thus forming new languages and phrases.

Bill Viola (1951 – Present)
| Artist Name | Bill Viola |
| Date of Birth | 25 January 1951 |
| Nationality | American |
| Associated Movements, Themes, and Styles | New media art, Contemporary art, consciousness, birth, and death |
| Mediums | Video art, sound, and mixed media |
Bill Viola is a renowned American new media artist who explores the relationships between consciousness, birth, and death through electronic sound and image technologies. Among his most famous works include Science of the Heart (1983) and Ascension (2000), which contributed to the acknowledgment of video art as a Contemporary art practice. Viola’s artworks often span entire rooms that immerse viewers into a visual and auditory landscape of art.
He has also created romantic scenes using traditional mediums alongside new media.

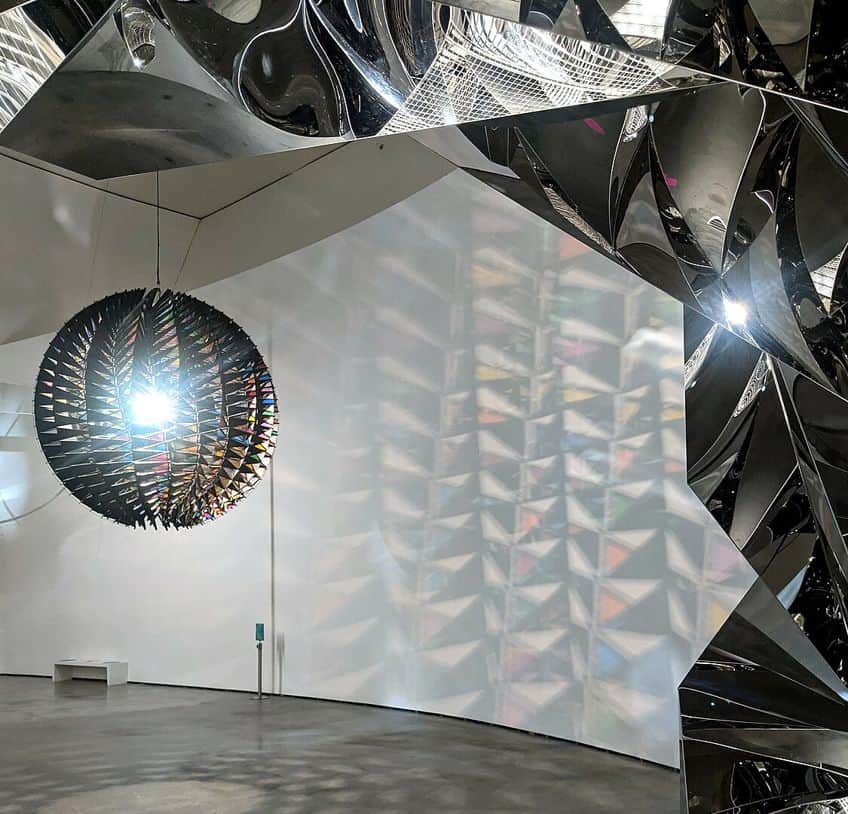
Olafur Eliasson (1967 – Present)
| Artist Name | Olafur Eliasson |
| Date of Birth | 5 February 1967 |
| Nationality | Icelandic–Danish |
| Associated Movements, Themes, and Styles | Contemporary art, new media art, immersive art, and environmental art |
| Mediums | Sculpture and installation |
Olafur Eliasson is a famous sculptor and installation artist who also established Studio Olafur Eliasson as a center for spatial research. Eliasson is renowned for his innovative approach to installation art, whereby he incorporates elements such as air, temperature, water, and light to create unique immersive artworks and experiences. Drawing from his experience in Iceland and Denmark, Eliasson highlights the relationships we have with sublime subjects and the ongoing environmental crisis humanity is constantly faced with. Eliasson’s work proposes ways in which artists can use their art to contribute to positive changes to curb the impacts of climate change.
Through simple mechanics, Eliasson’s large-scale sculptures and installations have earned him widespread recognition as a prominent artist of new media art.

Art Conservation and Preservation
As mentioned earlier, there is an ongoing need to preserve and conserve new media art, given the continuous technological improvements and the risks of maintaining the longevity of new media art. In new media art, a variety of approaches are used to preserve and conserve new media art and involve the “storage, migration, emulation, and reinterpretation” of new media artworks.
Below, we will discuss the challenges of preserving interactive and digital media artworks as well as a few strategies employed in the storage and preservation of new media art.
Challenges of Preserving Digital and Interactive Art
As the emergence of new media artwork grew around the mid-1990s, people began to recognize that new media artwork displayed different properties than that of physical artwork, and as such, the issue of storing such digital formats became a growing concern. One of the main issues with preserving new media artworks is that the formats of such works are continuously changing. These differ from analog technologies since digital files can be recopied into a completely new medium without any alteration to the content. One might notice such changes in modern-day transitions from portable hard drives to online cloud storage systems.

Since technology is always advancing, it is only natural that the structure of organizations and art institutions will be placed in jeopardy, since the traditional roles of the artist, curator, and viewer are constantly changing. In terms of the preservation of new media art, it is also wise to consider that new media artworks fall under the category called “complex digital objects”, as stipulated in the digital curation lifecycle model proposed by the Digital Curation Center. Another important aspect to consider is the storage of digital works that include performance art, internet artworks, and live electronic music, of which fails to capture the live context of the work as it is presented in real-time. Despite the challenges of storing and preserving new media art, there are a multitude of solutions, which we will look at below.
Strategies for Archiving New Media Art
Storing new media artwork also involves storing artworks in their original formats while maintaining the authenticity of the artwork. This means that you have to keep the metadata updated to locate and understand the different preservation strategies available to you now and in the future, and to adapt when necessary. To archive new media artwork also means to preserve it in some sort of way, and one can achieve this by migrating the original piece to a newer format, to enable ease of access in the future.
Using migration strategies is particularly important, especially if the artwork or file is saved on software such as Archive Space or Microsoft Word.
Another useful tool is Archivematica, which is a suite of open-source software tools that enables repositories to store files for a longer period, while also maintaining current industry standards. This is a useful tool to bridge the gap between the preservation and storage of the artwork. In addition to this, the Variable Media Questionnaire is another free web service that allows curators of new media artworks, and repositories, to share their strategies of preservation. This can provide you with helpful guidelines to preserve new media artworks once the original software becomes unavailable.
New Media Art in the Digital Age
Thanks to the internet and the development of social networking tools, one is better equipped to share and create new media artworks today, as compared to the past. Social media has proven to be one of the most efficient and easiest ways to share and create new media artworks that invite viewer participation and encourage interactivity. New media performances can also include social media activities that involve participation from a global audience while sharing the performance in real-time. However, the only major issue with creating new media artworks with social media is the storage and preservation of such content, which may not be long-standing for live events.

Artistic expression has capped itself at an all-time high with the widespread use of social media and its role in connecting humans and communicating important concepts. In some ways, social media has outperformed the role of the art institution in terms of accessibility and interactivity, which some art institutions can be clever enough to leverage in the 21st century. New media art also finds itself in the most basic online social interactions, including the creation of digital face filters that are produced in collaboration with various creative individuals and brands to promote art. Google Arts and Culture also encourages social interactivity with global institutions and a global audience by including interactive filters, with which many people interact and learn more about art.
New Media Art Festivals and Exhibitions
If you are a new media artist, exploring new media art festivals and exhibitions is a great way to network and meet new artists, while catching up on the latest technological advancements. There are numerous new media art festivals and exhibitions that invite a global audience and also feature brilliant talks on immersive art, sound, software-based artworks, and many interesting workshops and residencies. Festivals such as the SAT FEST, which was created by the Montreal-based Society of Arts and Technology, as well as MUTEK, are focused on international talent in digital art and electronic music.
The OFFF festival is another famous new media festival that began in 2000 and has since been hosted in 40 cities around the world to promote immersive digital art and design.

Such festivals are incredibly useful to attend to not only learn about current technological advancements that can enhance your art but also provide a diverse platform for discovering new talent. The NODE Forum for Digital Arts is one such new media event that offers programs and workshops to individuals to learn new skills while exhibiting the works of creatives from the analog and digital scene. The impact of such new media art festivals and exhibitions around the world has led to the formation of many artist collectives and groups who aim to bridge the gaps between science, technology, art, and new media.
New media art is an ever-shifting artistic genre that continues to provide new insights into how we interact and engage with art. By understanding what new media art is and how it can be used to propel contemporary concepts in line with current technological innovations, you can be sure to enhance your own Contemporary practice.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is New Media Art?
The contemporary understanding of new media art refers to any artwork produced using electronic media technologies. This can include computer graphics, animation, internet art, video games, 3D printing, digital art, robotics, and many other modern forms of technology that create unique human experiences for art. It is important to recognize that new media art is a broad genre of art that is continuously evolving in terms of its reliance on the latest media technologies.
What Are the Famous Forms of New Media Art?
There are many different forms of new media artwork. The most famous forms of new media art include virtual reality, augmented reality, computer animation, interactive art, video games, and internet art.
Which Famous Contemporary Artists Create New Media Art?
Among the most famous artists who created new media artwork include Nam June Paik, Alexei Shulgin, Cao Fei, Rafaël Rozendaal, Refik Anadol, Vera Frenkel, and Lu Yang, who have been recognized in the last five years for their contributions to new media art.
Liam Davis is an experienced art historian with demonstrated experience in the industry. After graduating from the Academy of Art History with a bachelor’s degree, Liam worked for many years as a copywriter for various art magazines and online art galleries. He also worked as an art curator for an art gallery in Illinois before working now as editor-in-chief for artfilemagazine.com. Liam’s passion is, aside from sculptures from the Roman and Greek periods, cave paintings, and neolithic art.
Learn more about Liam Davis and about us.
Cite this Article
Liam, Davis, “What Is New Media Art? – How Modern Technology Influences Art.” artfilemagazine – Your Online Art Source. September 11, 2023. URL: https://artfilemagazine.com/what-is-new-media-art/
Davis, L. (2023, 11 September). What Is New Media Art? – How Modern Technology Influences Art. artfilemagazine – Your Online Art Source. https://artfilemagazine.com/what-is-new-media-art/
Davis, Liam. “What Is New Media Art? – How Modern Technology Influences Art.” artfilemagazine – Your Online Art Source, September 11, 2023. https://artfilemagazine.com/what-is-new-media-art/.