Futuristic Architecture – Discover the Future of Building Design
Futuristic architecture is a term that can refer to many things. So, in this article, we’ll be breaking it down a little by looking at several different varieties of futuristic architecture, while also examining a few examples of 21st century futuristic buildings. This means that you should probably keep reading if you want to have a look at what has been called futuristic in the past, and what is futuristic right now.
A Look at Futuristic Architecture
A term like “futuristic architecture” is fundamentally broad in nature. The idea first arose in the early 20th century with the Italian Futurists, and they attempted to integrate this Futurism idea into a variety of art forms, like literature, painting, and sculpture. The idea was to effectively highlight the Machine Age, and this led to a number of issues as this movement was meant to be a way to fight against the traditional ways of doing things.
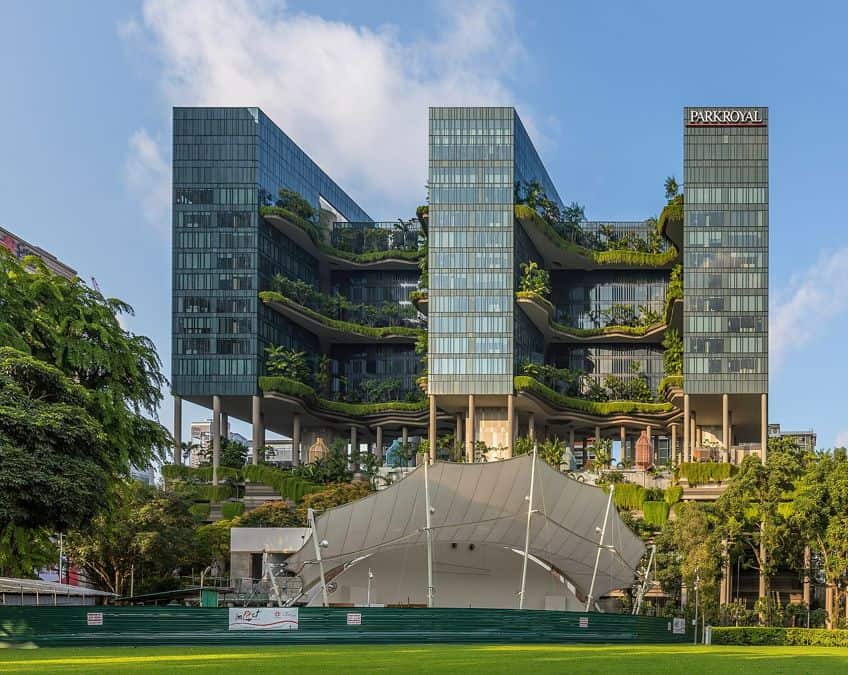

Some of the issues included a glorification of war and also an association with Mussolini’s National Fascist Party, the original fascists of the world, and so while not all Futurists or proponents of a similar ideology were fascistic in nature, the early movement was tainted with this association. This is a disappointing reality but one that cannot be easily denied.
However, ideas around Futurism and futuristic ideas, in general, did continue to blossom, and some of those ideas entered the field of architecture. After the fall of the Italian Futurists, these kinds of futuristic ideas and concepts did continue on in different parts of the world where they would grow and develop, but what even does “futuristic” mean in this case? Well, let’s have a look.
The Characteristics of Futuristic Architecture
The characteristics of something as broad as “futuristic architecture” cannot be easily defined, but one of the central ideas behind futuristic design, in general, is the use of technology for the development of architecture. It is a means of moving against the more traditional forms of architecture, like Neoclassical and Renaissance architecture. These forms are generally attempts to do something new.
Futuristic architecture entails the use of newer materials, newer designs, and newer techniques.
It does not want to emulate the past but rather aims towards something wholly new. However, what is considered new changes over time, and so while the earliest futuristic buildings may have made use of something like steel frames, that is no longer considered all that futuristic. So, let’s instead have a look at a few different types of futuristic architecture so that we can see how they interpret that overly general term “futuristic”.
The Many Varieties of Futuristic Architecture
We are going to examine seven different types of futuristic architecture in the following section. Some of these have their origins in the early 20th century, but others only truly started in the last twenty years of human existence. So, let’s have a look at some of the many varieties of futuristic architecture.
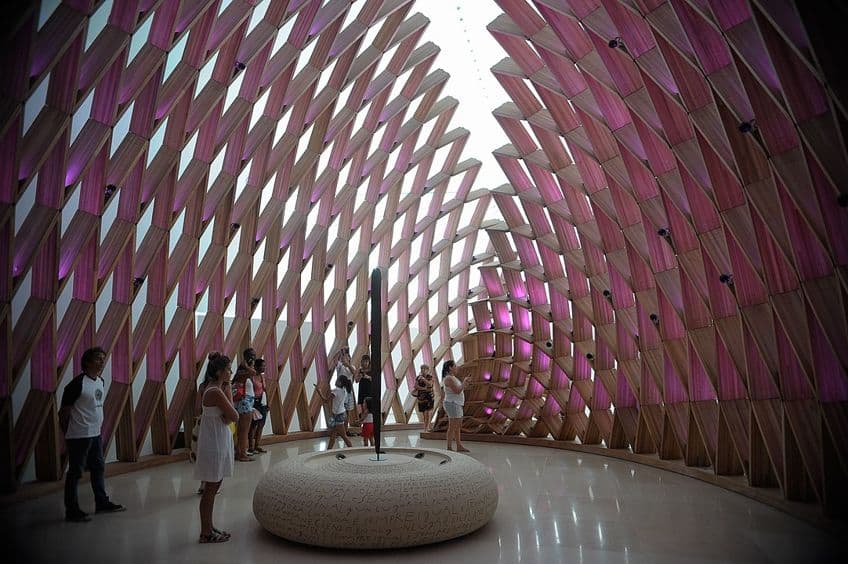

Art Deco Architecture
Art Deco architecture is one of the earliest forms of a so-called “futuristic” style of architecture. This particular form embraced a lot more than only architecture as it was used in a variety of mediums, from interior design to fashion to furniture. It has been an immensely influential art style that is, perhaps, best known for its architecture.
This form originated in France, but gained wide momentum in the United States, especially in New York City with structures like the Empire State Building.
Some of the principal characteristics of this architectural style include the use of highly stylized iconography like sunbursts and chevrons. However, other common elements included stepped designs, fluting around doors and windows, decorative panels, smooth wall surfaces, and a general aim toward linear structures.
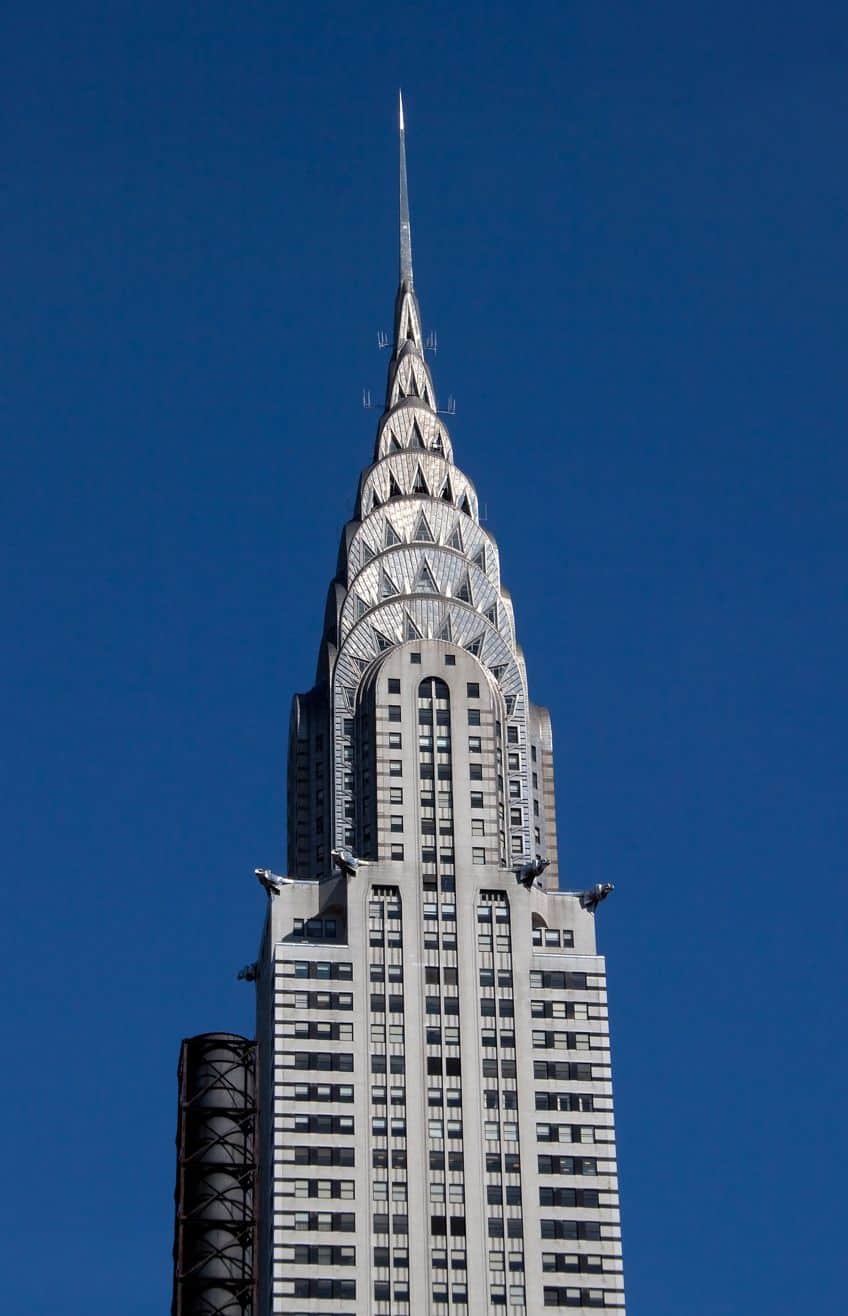

Googie Architecture
Googie architecture, first of all, has a rather hilarious name. The idea for this form of architecture came from a combination of scientific advances, such as the proliferation of cars and the shapes associated with them, the earliest jets, missiles, and rockets. The Atomic and Space Ages had a profound influence on this kind of architecture.
It would become especially associated with a specific view of the future and is perhaps best exemplified by pop cultural icons like The Jetsons.
In the modern day, this kind of architecture and general design is often labeled as a form of retro-futuristic aesthetics because of its immensely old-fashioned nature by more contemporary labels. Some of the primary characteristics of this architectural form included the use of geometric designs, upswept roofs, and curve-oriented designs. Another immensely common feature was the extensive use of materials like neon, steel, and glass, and many of these styles can still be seen to this day in cities like Las Vegas.

Parametric Design Architecture
Parametric designs are not inherently architectural in nature but have been used in them for the last few decades. The general idea behind these designs is that they are not particularly easy or even possible to design by hand, instead, they are designed through the use of algorithms.
Some of the earliest forms were developed in the 1980s, but they have become more prevalent as these forms of architecture have become more possible through increasingly advanced computer technology.
These parametric designs often feature many curved and hollowed forms where the materials need to be specifically designed so that they remain load-bearing despite the designs strewn across their surfaces. This architectural style is generally designed using software like Autodesk Maya, GenerativeComponents, and Marionette. This architectural form has an immediate “futuristic” appearance, and as it can be used in large-scale structures that appear as if they should otherwise collapse, the Futurism label is likely well-earned.
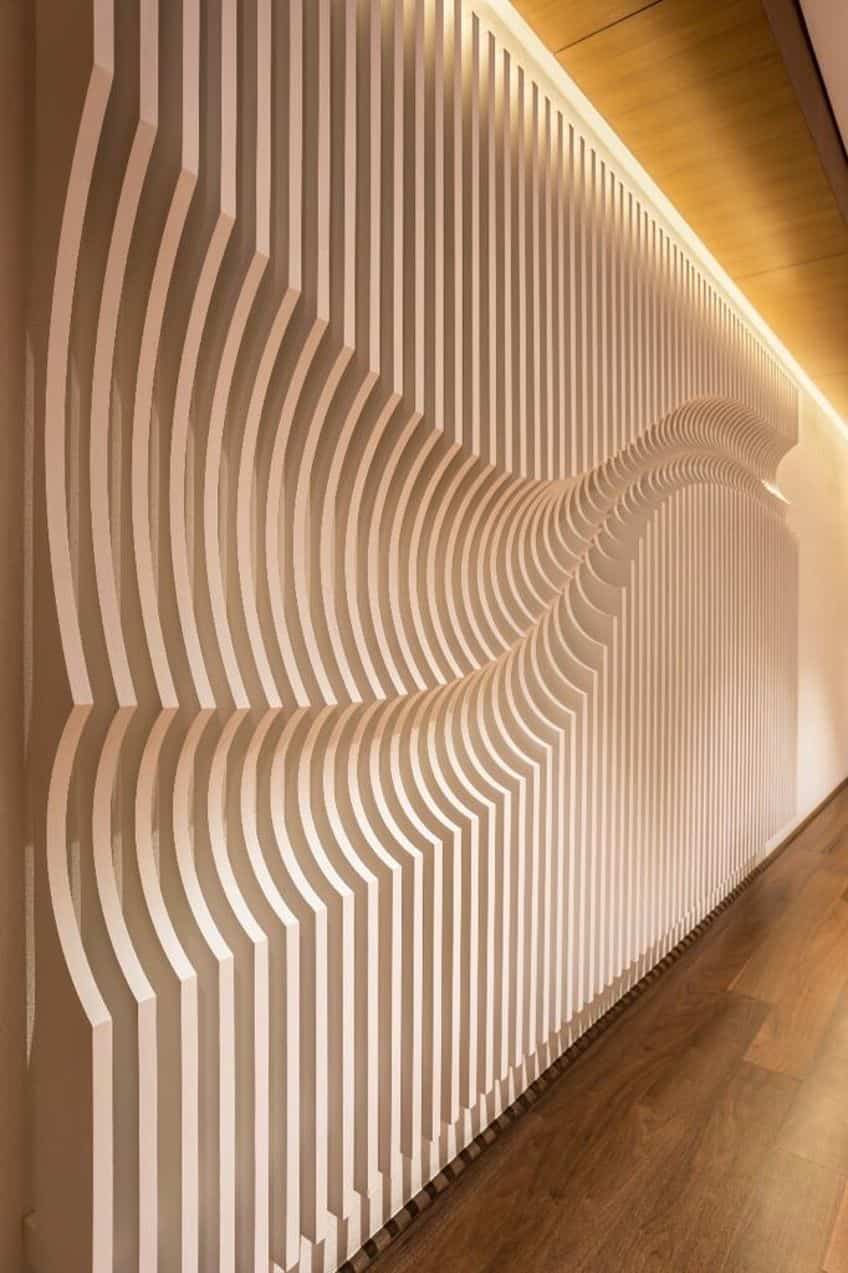

Neo-Futuristic Architecture
Neo-Futurism is the form that perhaps best attempts to be explicitly “futurist” in its design. Neo-Futurist architecture is often considered to be a form of avant-garde architecture (as is likely a common attribute applied to all forms of futuristic architecture).
It has become increasingly used throughout the world because this architectural movement entails an attempt to unify aesthetics and functionality within a new paradigm.
One of the principal characteristics of this form is not any particular architectural features but rather an attempt to mix artistry, the latest technologies, and a desire for a higher quality of life into structures. This form of architecture has been used in many contemporary structures that are meant to be both economically viable and ecologically sustainable. One of the most famous buildings that adopt a Neo-Futurist style is the Burj Khalifa in Dubai.
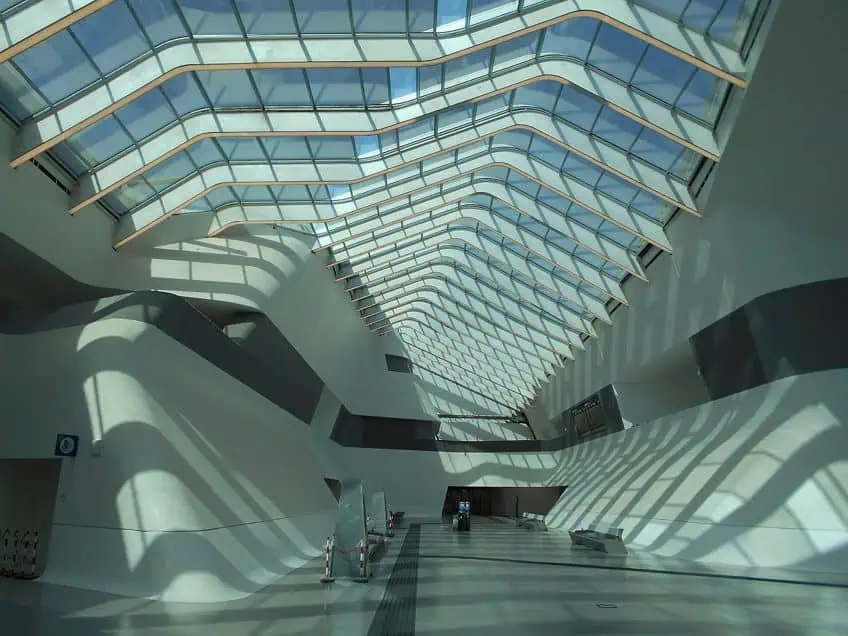

High-Tech Architecture
High-tech architecture is essentially what it says on the tin: it is an attempt to implement the latest technology into buildings. The general idea arose out of Modern architecture, which was also an attempt to use the latest technologies, but this newer form typically attempts to use technologies associated with contemporary-era materials, like aluminum but also things like steel and glass.
These last two older forms are generally implemented in far more high-tech ways, such as through specifically tempered steel and newly reinforced or reflective forms of glass.
The buildings that adopt the high-tech style usually do so to progress to a more technologically savvy means of architecture that does away with many of the traditional styles. You won’t find any traces of older forms of architecture within the influences of these structures. They tend to lack internal load-bearing walls, have internal spaces that can be rearranged, and implement brightly colored aesthetics to project the illusion of a diagram-oriented design.

Blobitecture
Blobitecture, like Goobie architecture, is a cute name. It comes from the general idea of “blob architecture”, which is the creation of buildings that adopt a more organic form that typically looks like, you guessed it, a blob. These buildings first started to truly appear in the mid-1990s, but they started to become even more prominent throughout the 2000s.
This form of architecture is yet another futuristic architectural design that is often not possible without the use of computers.
The curved designs and blob-oriented nature means that determining load-bearing structures can be difficult without software geared toward that kind of design. So, even though blobitecture has a far more organic look than many other forms of more traditional architecture, it would be practically impossible without the use of advanced computer systems. The style does tend to be seen as rather strange though, even by today’s standards.
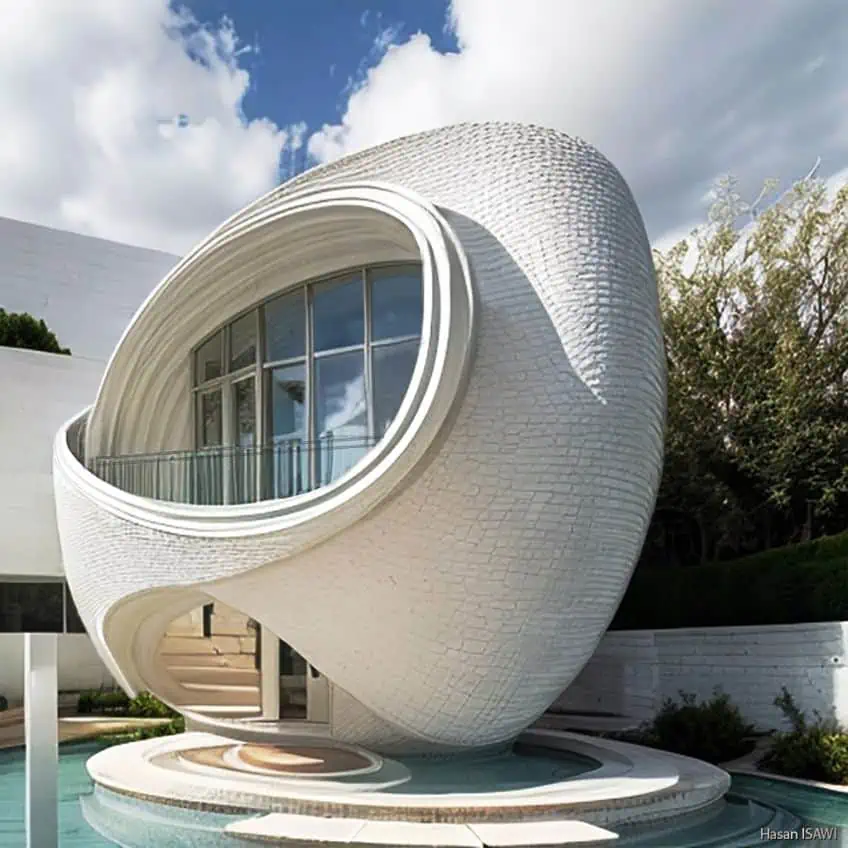

Sustainable Architecture
Sustainable architecture is one of the more recent forms that have become immensely popular over the last two or so decades. The planet Earth is currently in crisis as climate change is a constantly escalating threat, and so the architecture of this variety is typically constructed to be a response to that need. Sustainable architecture usually adopts sustainable construction practices, uses recycled materials, produces its own electricity, uses ecological forms of heating and cooling, and some even recycle their own water.
So, the basic idea is to make buildings that are, essentially, off the grid. If a building doesn’t need to draw power from a national grid or water from a local source, then that building does not impact the environment around it.
This is a more ecological attempt to produce a form of livable architecture that does not damage the planet on which we live. Some of the most stunning examples of this in the present day are the vertical garden-style buildings that have become increasingly prevalent, like Tao Zhu Yin Yuan in Taipei.
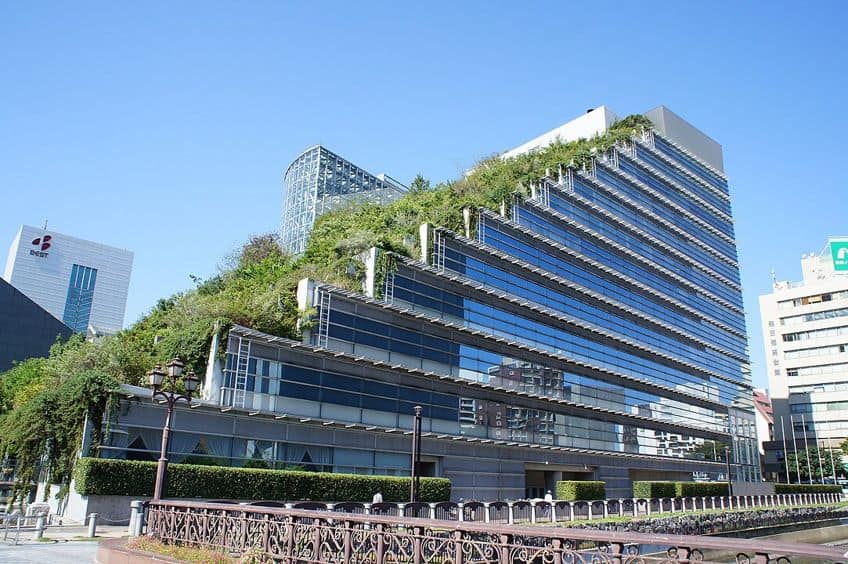

These are only some of the forms of futuristic architecture that have developed in an attempt to chase a future that may just happen. Many of the latest forms of futuristic architecture have adopted a sustainable model, and so sustainable architecture is possibly the most common of these forms of architecture at the time of writing. However, it would probably be best to examine some of those futuristic buildings to see for ourselves.
Examples of Futuristic Buildings
While the general idea of a “futuristic design” is a very nebulous and broad idea, as “futuristic” inherently changes as time goes on, we will have a look at some examples of more futuristic building designs in the 21st century.
Even those who are unimpressed by the existence of various supposedly “futuristic buildings”, should be at least partially impressed by these newer structures.
Burj Khalifa (2004 – 2009) in Dubai
| Architect | Adrian Smith (1944 – Present) |
| Date Constructed | 2004 – 2009 |
| Function | Mixed-use |
| Location | Dubai, United Arab Emirates |
The Burj Khalifa is an example of Neo-Futurist architecture, and it is one of the most advanced skyscrapers in the world. This massive skyscraper can be found in Dubai, and it stretches 829.8 m (or 2,722 ft) into the sky. This is one of the most futuristic skyscrapers in the world because of its economical and ecological design as well as the general appearance that it was designed to possess. It is also the tallest building in the world at the time of writing, and it has been the tallest ever since it was topped out in 2009.
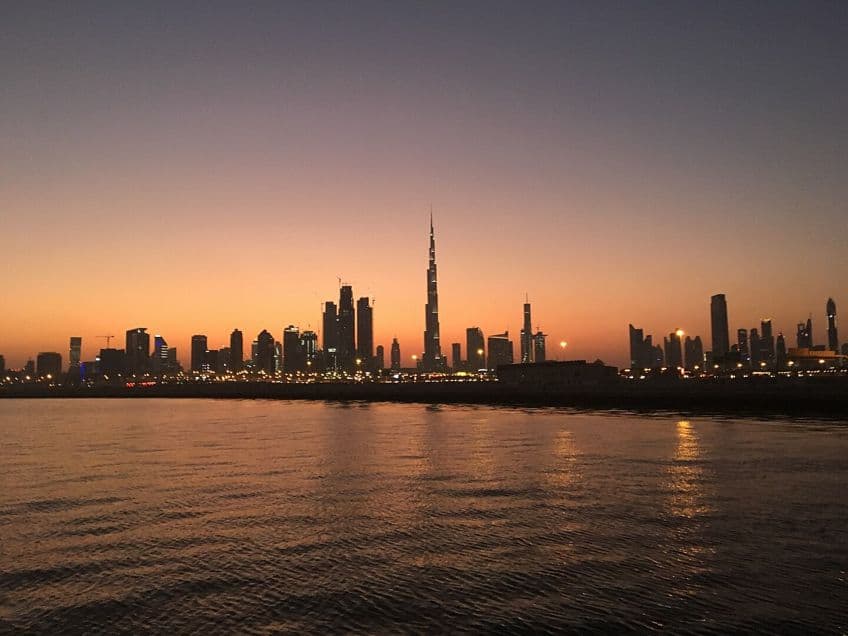

The futuristic design of the Burj Khalifa can be found in the manner in which the skyscraper is derived from, and adapts, the local Islamic architecture in much of its general design, but it also adopts an unusual Y-shape for its floor plan to maximize internal space. Other inventive techniques that were employed in this futuristic skyscraper include the bundled tube design that allowed for half the ordinary quantity steel to be used than would have been ordinarily used in a structure of this size, and thereby led to the construction of this building to be immensely ecologically safe in comparison to many other skyscrapers.
Thanks to the building’s location in the desert, it needed to be designed in such a way as to minimize the potential dangers of its geographical situation.
This is why the Burj Khalifa makes use of setback designs that reduce wind vibration, and it makes use of special reflective glass panels to reduce the overall solar burden on the structure while implementing anti-glare technologies too. The Burj Khalifa makes use of many techniques to help it survive the terrain and supply itself with some of the necessities of life in general. It’s a sustainable skyscraper that minimizes its carbon footprint in many ways. All of this means that the Burj Khalifa will ultimately serve as a model for futuristic skyscrapers for decades to come.
Pixel Building (2010) in Melbourne
| Architect | studio505 |
| Date Constructed | 2010 |
| Function | Office building |
| Location | Melbourne, Australia |
The Pixel Building is a particularly odd-looking structure in the middle of Melbourne. This building was designed as a piece of sustainable architecture and construction. It features a futuristic building design that appears strange to us because of its immense irregularity from standard buildings. The thing that really sets it apart is that it is covered in strange multi-colored panels. These panels may, at first, appear entirely aesthetic and fitting in with the pixel art aesthetic that the building appears to exude, but those panels actually allow the maximum amount of light while reducing glare and heat in the building.
So, the Pixel Building may look like it has an inherently futuristic design, and it certainly does, but that futuristic design is not purely aesthetic. It is the combination of aesthetics, architecture, and engineering to produce something that stands as the country’s very first carbon-neutral office building.
It was constructed using low-carbon concrete and a variety of recycled building materials, and so the construction itself was more sustainably done than most, but the completed building is also an ecological marvel. The building is not connected to the water mains of the city because it reduces rainfall water. It also produces its own electricity through the use of wind turbines and even solar panels on the roof. The solar panels even move with the sun to maximize the amount of energy that is processed by the building. There is even an air-cooling system within the structure that is ecologically safe to use. While the outside of the Pixel Building may have an avant-garde appearance, the interior of the structure is a stunning example of sustainable futuristic design.
The aesthetics of it all may not be to everyone’s tastes, as it is extremely colorful, but it is a good step forward in terms of the kind of sustainable architecture that will likely become more and more necessary as time goes on for our world.
Museum of Tomorrow (2011 – 2015) in Rio de Janeiro
| Architect | Santiago Calatrava (1951 – Present) |
| Date Constructed | 2011 – 2015 |
| Function | Museum |
| Location | Rio de Janeiro, Brazil |
The Museum of Tomorrow is a museum in Rio de Janeiro, and it is an explicit example of Neo-Futurist architecture as it was designed by a man noted for his Neo-Futuristic designs. This stunning example of futuristic architecture is a science museum that includes five main areas within its walls. These five areas look at everything from the cosmos themselves to the earth that humans have influenced to the possible future that we have created for ourselves.
The exhibitions in the museum contain many arguments for sustainable development going forward, and from the building’s position beside the city’s port, it can be seen by those who enter the city via the ocean. This building was actually part of a rejuvenation effort in preparation for the FIFA World Cup in the country, and the port was a location that especially needed an overhaul because of its position as a dangerous location in Rio de Janeiro.
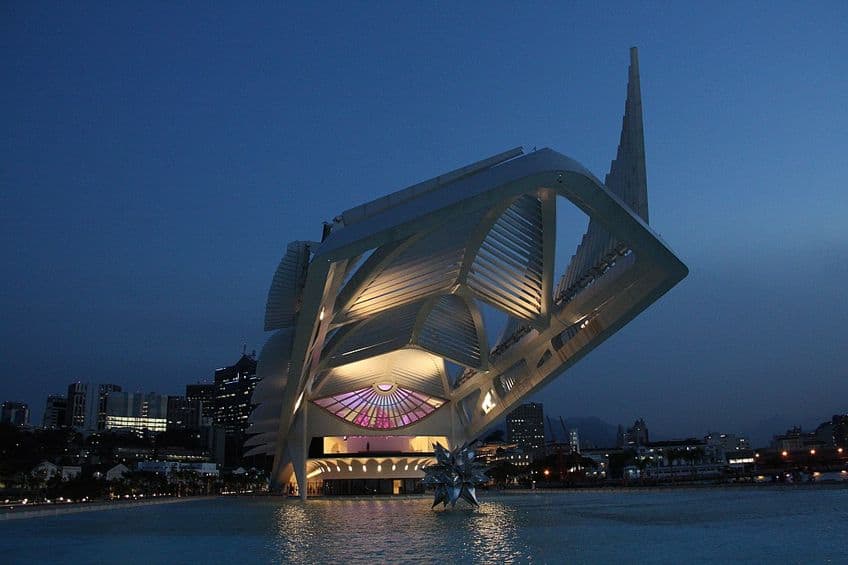

The museum is designed to be entirely white and there is a unique and protruding canopy that extends from the entrance. The architect, Calatrava, stated that he was inspired by bromeliads (which are plants native to the region) when he was designing the building. This works well with the aim towards sustainability and futuristic architecture as many instances of futurism architecture look towards the natural world for inspiration. Some of the other primary features that contribute to that sustainability aspect include the solar panels that move with the sun to maximize the amount of light that can be used and it also reuses rainwater.
So, this museum is a stunning example of sustainable architecture even though that may not be the first thing you think when you see it for the first time.
Amager Bakke (2013 – 2017) in Copenhagen
| Architect | Bjarke Ingels Group |
| Date Constructed | 2013 – 2017 |
| Function | Waste-to-energy plant |
| Location | Copenhagen, Denmark |
Amager Bakke is a fascinating structure because of how unlike anything else it manages to be. When you first see this building, which is also known as Copenhill and Amager Slope, it appears to be a dry ski slope for those who want to do some skiing practice all year round. However, when you take a closer look, you start to see that it’s actually a factory of some sort with a ski slope as a roof.
This utterly bizarre design is because the building is actually a waste-to-energy power plant that also doubles as a recreational area within the city. The roofing structure contains a lot more than just a ski slope though. It also features a hiking trail and even a climbing wall (which also happens to be the tallest of its kind in the world).
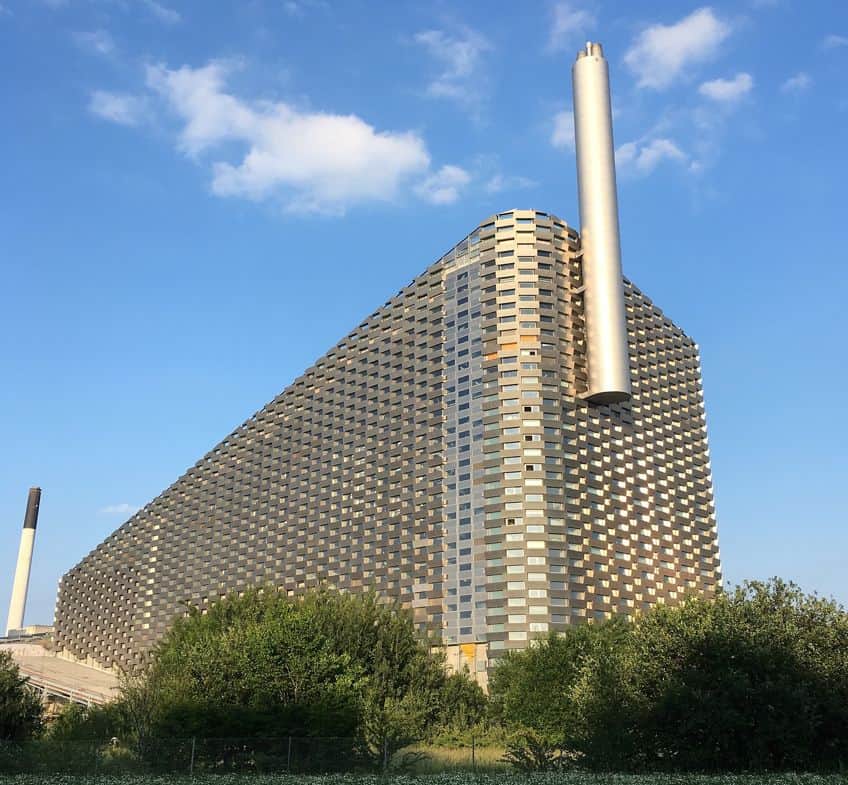

So, what would otherwise be a rather ugly building in the middle of Copenhagen, a power plant, has been transformed into a usable feature for social good. It even includes a park and play area on its roof, and you’ll be able to get a great view while doing it too. All of this is part of Copenhagen’s goal to be the world’s very first carbon-neutral city by 2025. They don’t have much time at the time of writing, but structures such as this serve as a good move towards that aim. The recreational aspect of this structure obviously gets the lion’s share of the attention, but the building itself also does incredibly important work by transforming waste products into clean energy.
Power plants of this nature need to become more commonly used in the future, and buildings like Amager Bakke will help in presenting a way for us to do just that.
Tao Zhu Yin Yuan (2013 – 2018) in Taipei
| Architect | Vincent Callebaut (1977 – Present) |
| Date Constructed | 2013 – 2018 |
| Function | Residential |
| Location | Taipei, Taiwan |
The Tao Zhu Yin Yuan is a piece of futuristic architecture that also serves as a high-rise residential building and a vertical garden structure. The building is not exactly an example of a futuristic skyscraper at only 93.2 m (or 306 ft), but it does have a gorgeous plant-based aesthetic all the way to the top. The idea behind this structure was to produce a building in a double helix design that emulates a strand of DNA, and so every floor is differently angled to produce the rotated aesthetic. This DNA building is also covered in a variety of trees and bushes that extend upwards and absorb about 130 tons worth of carbon dioxide emissions for the city.

The building aids in the reduction of the carbon footprint of the city, but it also aims to create a structure that brings both humans and nature together in a sustainable fashion. It makes use of low energy consumption technologies, reduces water, recycles organic waste for its gardens, and it even allows for the residents to farm the organic food that is created by the plants. Architecture, in general, tends to be an attempt to move civilization further away from the natural world, but structures like this attempt a far more positive approach to nature by integrating with it instead of trying to keep it at bay. These kinds of residential buildings will hopefully become more prominent in the next few decades as we move towards more and more sustainable development across our world.
We have come to the end of our discussion about futuristic architecture. We looked at some of the different types of futuristic architecture and their specific characteristics, and then we had a look at a few specific futuristic buildings from the 21st century and what makes them tick. Hopefully, you’ve learned a good deal about futuristic architecture in general. All that’s left to do is to wish you a great day/week/month ahead!
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is Futuristic Architecture?
Futuristic architecture is a very broad and often generic label that refers to architecture that is, in some way, an attempt at creating something futuristic in general. It’s a way to refer to buildings that go against some of the strains of more traditional styles of architecture, while also aiming towards some kind of a view of what the future will be. This is why there are many different styles of futuristic architecture, from Art Deco to High-tech architecture to sustainable architecture.
When Did Futuristic Architecture Develop?
The earliest Futurists were the Italian Futurists in the early 20th century, but their work has not necessarily influenced all subsequent futuristic forms of architecture. Instead, a number of styles developed over time, such as Art Deco, which is often considered to be one of the oldest forms of futuristic architecture, but many other forms have developed over the decades. So, this is more of an indication of a general viewpoint in architecture rather than a specific style with unifying characteristics.
What Is the Most Famous Futuristic Building?
This is difficult to say, but as Art Deco is considered to be a form of early Futurism architecture, it may be easiest to say that the most famous Art Deco building also doubles as the most famous futuristic building. If this is the case, then the most famous futuristic building could arguably be identified as the Empire State Building in New York City.
Justin van Huyssteen is a writer, academic, and educator from Cape Town, South Africa. He holds a master’s degree in Theory of Literature. His primary focus in this field is the analysis of artistic objects through a number of theoretical lenses. His predominant theoretical areas of interest include narratology and critical theory in general, with a particular focus on animal studies. Other than academia, he is a novelist, game reviewer, and freelance writer. Justin’s preferred architectural movements include the more modern and postmodern types of architecture, such as Bauhaus, Art Nouveau, Art Deco, Brutalist, and Futurist varieties like sustainable architecture. Justin is working for artfilemagazine as an author and content writer since 2022. He is responsible for all blog posts about architecture.
Learn more about Justin van Huyssteen and about us.
Cite this Article
Justin, van Huyssteen, “Futuristic Architecture – Discover the Future of Building Design.” artfilemagazine – Your Online Art Source. August 10, 2023. URL: https://artfilemagazine.com/futuristic-architecture/
van Huyssteen, J. (2023, 10 August). Futuristic Architecture – Discover the Future of Building Design. artfilemagazine – Your Online Art Source. https://artfilemagazine.com/futuristic-architecture/
van Huyssteen, Justin. “Futuristic Architecture – Discover the Future of Building Design.” artfilemagazine – Your Online Art Source, August 10, 2023. https://artfilemagazine.com/futuristic-architecture/.