Famous Asian Paintings – A Closer Look at Ancient Asian Art
What is Asian art? What are the characteristics of Asian art? Who are the most popular ancient Asian artists? What can we learn from famous Asian artworks? These are just some of the questions that you will find the answers to in this article. Asia is an incredibly diverse continent with many historically marginalized cultures that have produced some of the most exquisite artworks in art history. Read on to discover some of the most famous Asian paintings from the ancient and Contemporary Asian art world.
Contents
Traditional Asian Art: A Diverse Spectrum
What is Asian art? Asian art, from a traditional context, refers to art produced in ancient Asia and includes different art forms from various cultures across South Asia, Southwest Asia, East Asia, and Southeast Asia. Below, you will find a table summarizing the different regions in Asia and their corresponding periods, which are considered to be part of ancient Asia to help you contextualize the artworks discussed below.
| Ancient Asian Region/Dynasty/Era | Locations | Time Period |
| Ancient Near East | Mesopotamia, Egypt, Iran, Anatolia/Asia Minor, Armenian Highlands, Levant, Cyprus, and the Arabian Peninsula | 4th Millenium BCE – 7th Century CE |
| Iran (Greater Iran) | Anatolia, the borders of ancient India, Syr Darya, Caucasus, Eurasian Steppe, Persian Gulf, Gulf of Oman, and Persia (Iran) | 10,000 BCE – 16th Century |
| Elam (Susiana) | Khuzestan, Ilam Province, and South Iraq | 3000 BCE – 224 CE |
| Western Asia: The Achaemenid Empire (First Persian Empire) | Balkans, Egypt, Central Asia, Indus Valley, and Persis | 550 BCE – 334 BCE |
| Ancient India, Indus Valley, Iron Age India | Mehrgarh, Indus Valley, Punjab, Gangetic Plain, Greater Magadha, Kannauj, Sri Lanka, the Maldives, Bengal, and Mewar | c. 2 million BCE – 1526 CE |
| Iron Age China | Changsha, Nangjin, Yangtze Valley, and Lingnan | 10th Century BCE – 7th Century BCE |
| Spring and Autumn Period (China) | Lu, Haojing, Yellow River Valley, Chengzhou, Qin, Jin, Qi, Chu, Wu (Jiangsu), and +148 states | 770 BCE – 476 BCE |
| Western Han, Eastern Han (Golden Age of China) | Chang’an, Luoyang, and Xuchang | 202 CE – 225 CE |
| Proto-Three Kingdoms of Korea and Three Kingdoms of Korea | Korean Peninsula: Byeonhan, Jinhan, and Mahan | 57 BCE – 668 CE (proto-three kingdoms) and 18 BCE – 660 CE (three kingdoms) |
| Kofun Period, Asuka Period, Nara Period, and Heian Period (Japan) | Southern Korean Peninsula, Kyūshū, Honshū, Nara (Makimuku district), Tanegashima, Yakushima, Tainai (Niigata Prefecture), Kibi (Okayama Prefecture), Izumo (Shimane Prefecture), Kenu (Northern Kantō), Koshi (Fukui/Niigata Prefecture), Baekje, Asuka, Heian-kyō (Kyoto), Northern Honshu, and Hiraizumi | 250 CE – 1185 CE |
| Vietnam (Thục Dynasty to the Second Era of Northern Domination) | Âu Lạc (Red River Delta), Văn Lang, and Long Biên | 208 BCE – 544 CE |
| Mainland Southeast Asia and Maritime Southeast Asia | Cambodia, Laos, Peninsular Malaysia, Myanmar, Thailand, Vietnam, Cocos Islands, Brunei, East Malaysia, Christmas Island, Singapore, Indonesia, Philippines, and East Timor | 50,000 BCE – 13th Century (European Colonization) |
Asian art encompasses art from multiple regions across Asia and spans multiple mediums. Some of the earliest paintings have been discovered in Asia as well as important traditional artwork that has left a strong influence on the artistic quality of what many consider to be traditional Asian art. Below, we will take a look at a few characteristics of Asian art, in the context of the dominant artistic regions.
Dominant Characteristics of Asian Art
Asia is one of the richest continents of artistic legacy and cultural productions, which continue to hold a significant influence on the Contemporary art scene. Many important artworks from Asia demonstrate not only the artistic quality of art in Asia throughout the centuries since its occupation by early Homo sapiens, but also illustrate the cultural diversification and expansion across multiple regions that have also influenced each other.
The Chinese Influence
The characteristics of Asian artworks are numerous and specific to the region, period, and culture in which they were produced. Some of the most prominent characteristics of art from ancient China include the use of jade in sculpture as well as major art forms such as painting and calligraphy, which were at the forefront of ancient Chinese art.
Similarly, the ancient art of Japan also placed importance on the finer decorative arts and reflects the early culture’s interaction with other cultures.
Another driving force behind Asian art was the emergence of Buddhism, which shed light on the visual arts and spiritual practices of many people. The Chinese Zen aesthetic is one such visual influence that found its way to Japan and sparked a trend in monochrome ink paintings in Japan during the Muromachi period (1338 – 1573).
Early Vietnamese Art Styles
Like many early Asian cultures, Vietnamese art also saw its artistic development in pottery and sculpture with incredibly detailed incisions for decoration and eventually scenes from everyday life. Vietnam was also influenced by Chinese culture around the early 2nd century and absorbed some of its influences. It is said that the Vietnamese Golden period in art occurred in the Ly Dynasty era (1010 – 1225), when Vietnamese-made ceramics gained widespread popularity across Southeast Asia and far out to the Middle East.

Early Korean Art Styles
Artistic development in the Three Kingdom period of Korea was also driven by the introduction of Buddhism from China by 372 CE and was translated visually into architecture, statues, reliefs, terracotta sculptures, and sculptures made from jade and ivory. Religious art dominated this part of Asia from the 6th to the 15th century and was the source of the most important themes in Korean art history.
Many artists, later on, went on to incorporate the painting techniques of the West with the ancient practices of the East, resulting in rich and symbolic paintings with a Contemporary edge that can still be seen in the works of many Asian artists today.
The Near East
Between 4000 BCE and 500 CE, art from the Near East regions was centered around objects and artifacts that symbolized wealth and power, a characteristic that was heavily driven by the artistic influences of the ancient Egyptians. Art from these regions was documentative and portrayed key events in history, laws, everyday practices, and decorative qualities.

Similarly in ancient Iran, better known as Persia, calligraphy, and metalwork played an important role in the lives of its civilization. Persian art greatly influenced the development of Islamic art and focused on subjects such as royal figures, the human form, and animals. The art from this region was also at one point characterized by the combination of motifs from Islamic art and Chinese culture.
Ancient Indian Art Styles
Ancient Indian art in Asia consisted of intricate textile work and is most recognized for its variety in ceramics, pottery, woven silk, and painting. Design was prevalent in ancient India with its roots in art dating as far back as the third millennium BCE. Religious influences on ancient Indian art include Sikhism, Islam, Jainism, Buddhism, and Hinduism.
The influence of each region in Asia was shared and interconnected at different points in time, which makes exploring the traditional art of Asia so interesting.
The Most Famous Asian Paintings of All Time
The world of Asian art is jam-packed with cultural diversity and a wealth of artistic styles and modes of production from which we can draw inspiration from. Below, we will examine the top 10 most famous paintings from the ancient historical record to the 21st century.
Top Five Most Famous Asian Paintings From Ancient History
The earliest oil painting was discovered in Asia, in Afghanistan caves, which depict Buddhist imagery and date back to 650 CE. Oil painting was long thought of as a medium that developed in Europe, however, its true birthplace in Asia, is an important beacon that points to the significance of the continent in the broader context of artistic and cultural production. Below, you will find a list of some of the most famous Asian paintings in history that demonstrate the artistic development of early Asian art.
Nymph of the Luo River (c. 344 – 406 CE) by Gu Kaizhi and Dong Qichang
| Artist | Gu Kaizhi (c. 344 – 406); copy by Dong Qichang (1555 – 1636) |
| Date | Original: c. unavailable (est. 344 – 406 CE); and copy: est. 1555 – 1636 |
| Medium | Ink and color on silk handscroll |
| Dimensions (cm) | 24.1 x 310 |
| Where It Is Housed | Smithsonian, National Museum of Asian Art, Washington D.C, United States |
This famous silk handscroll painting was created in the Jin Dynasty, originally by one of the most famous Chinese painters in Asian art history. Gu Kaizhi is known as the father of Chinese painting and was an incredibly influential artist to many. This famous Asian painting, Nymph on the Luo River, was reproduced as a copy of the original imagery by another Chinese artist and politician known as Dong Qichang of the Song Dynasty.
While there are no original traces of Gu Kaizhi’s original works, an understanding of his style and subject matter from the Jin Dynasty can be understood and analyzed through this copy.
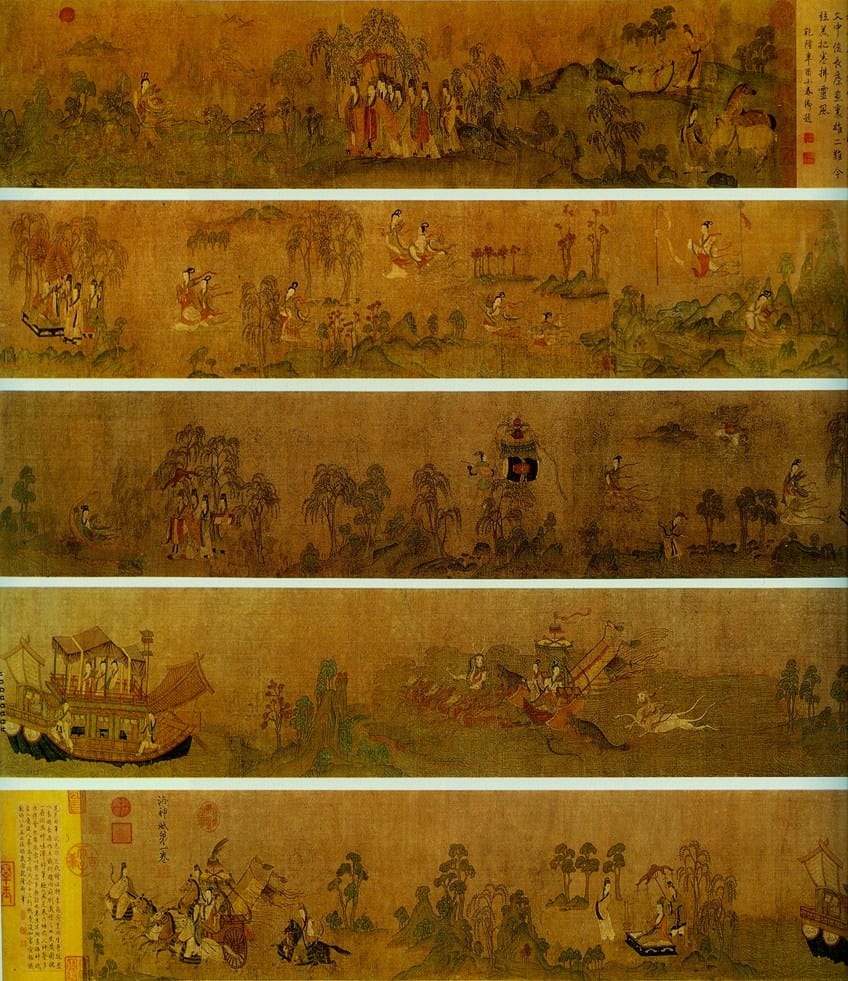

Nymph on the Luo River is a painting inspired by a poem written by Prince Cao Zhi in 222 CE. The poem was based on the romantic tale of the prince himself who fell in love with an imaginary nymph (or goddess) at the Luo River. The two lovers parted ways in the end and the imagery in the painting beautifully illustrates not only the gentle nature of the two figures involved but also the breezy environment surrounding the loving couple.
The painting was executed with such a strong grasp and connection to emotion that its visual translation relays the sense of “love is in the air”.
This is only a glimpse into what the original copy of the painting may have looked like. For Gu Kaizhi, the defining aspects of painting were translating the spirit and essence of the figures involved as opposed to the clothing and superficial depiction of the subject.
The Madhubani Wall Paintings (8th – 7th Century)
| Artist | Unknown |
| Date | 8th – 7th Century |
| Date of Discovery | 1934 |
| Location | Madhubani district, Bihar |
| Medium | Powdered rice, paint, mixed media |
| Dimensions (cm) | Unavailable |
Loaded with symbolism and animal imagery, these incredible wall paintings were discovered in 1934 by the colonial officer, William G. Archer, who inspected the Madhubani district after a massive earthquake. These types of paintings were traditionally created by women from Brahmin and Kayastha and only received appreciation in the latter half of the 20th century with the increased publicity for the art form.
It is believed that the style for Madhubani paintings originated around the 8th and 7th centuries and was commonly practiced in the Mithila region of Bihar and Nepal.

The wall paintings in the Madhubani district were found in houses with walls coated in cow dung, which acted as a preservative. The paintings were created using paint and pulverized rice and then coated with hands and detailed with bamboo twigs and cotton rags. Madhubani paintings contain complex patterns and the imagery usually occupies the entire space.
Some of the imagery traditionally depicts animals, decorative motifs, mandalas, and various significant symbols, including the snake (symbolizing regeneration), the lotus aripana (sexual energy), and the circle aripana (God of creation).
Genji Monogatari Emaki (c. 1120 – 1140): A National Treasure of Japan
| Artist | Unknown |
| Date | c. 1120 – 1140 |
| Medium | Ink and color on paper scroll |
| Dimensions (cm) | Original (20 rolls): 13716; +100 paintings, 300 calligraphy sheets; and surviving: 19 paintings, 65 calligraphy sheets, and 9 fragments |
| Where It Is Housed | Tokugawa Art Museum and Gotoh Museum, Nagoya, Japan |
The Genji Monogatari Emaki, most commonly known in English as the Tale of Genji scroll, is the most famous and oldest painting in Japan. The original scroll was roughly 137 meters long and contained a collection of over 100 paintings and 300 calligraphic sheets with texts by different artists. What remains of this famous and lengthy collection are only 19 paintings and 65 calligraphic sheets, executed in a pictorial technique identified as tsukuri-e, which translates in English to “manufactured painting” and is considered an expansion of the former design style Yamato-e.
The painting is currently divided into two portions and located at two separate museums in Japan with one section at the Tokugawa Art Museum in Nagoya and the Gotoh Museum in Setagaya’s Kaminoge district.
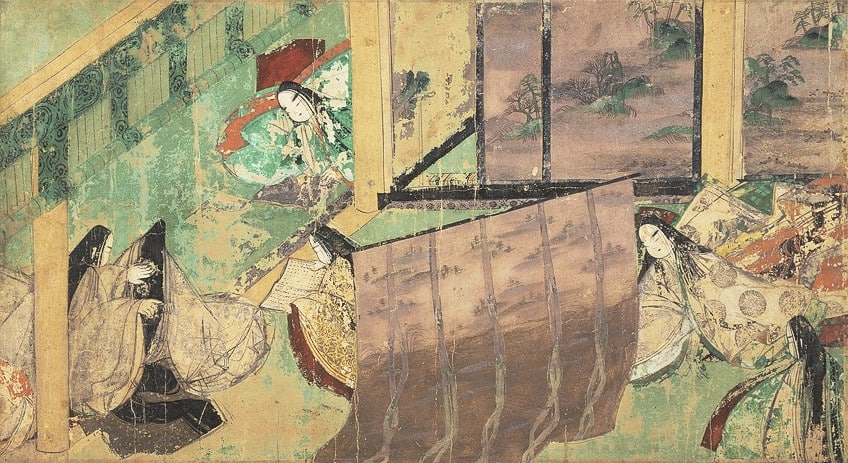

Both institutions are private institutions, which only exhibit the painting for brief durations due to the fragility of the painting. The scroll is also considered to be a National Treasure of Japan and is the first known narrative-illustrated scroll of the Yamato-e tradition.
Aside from the calligraphic techniques of the artists, which are significant in their own right as an art form, one can also admire the emotional quality behind the faces of the paintings’ subjects.
It is believed that these early artists used a technique called hikime kagibana to illustrate faces and altered the sizes of the figure’s facial features to draw out emotion. This can be seen in seemingly minute changes such as the distance between the eyes or the eyes and the eyebrows. A painting of Lady Kumoi in one of the paintings is one such example of how Japanese artists of the 12th century brought out the character of their subjects.
Tiger From the Joseon Dynasty
| Artist | Unknown |
| Dynasty | Joseon Dynasty (1392 – 1897) |
| Medium | Ink on paper |
| Dimensions (cm) | 97.6 x 55.5 |
| Where It Is Housed | National Museum of Korea, Seoul, South Korea |
This famous tiger painting is one of the most unusual and famous paintings from ancient Korea, which depicts a large tiger painted across the entire scroll sheet. In ancient times, tigers were usually depicted in landscape settings and were symbols used to ward off evil energies.
This painting is considered to be one of the best masterpieces in the National Museum of Korea, dating back to the Joseon Dynasty (1392 – 1897).
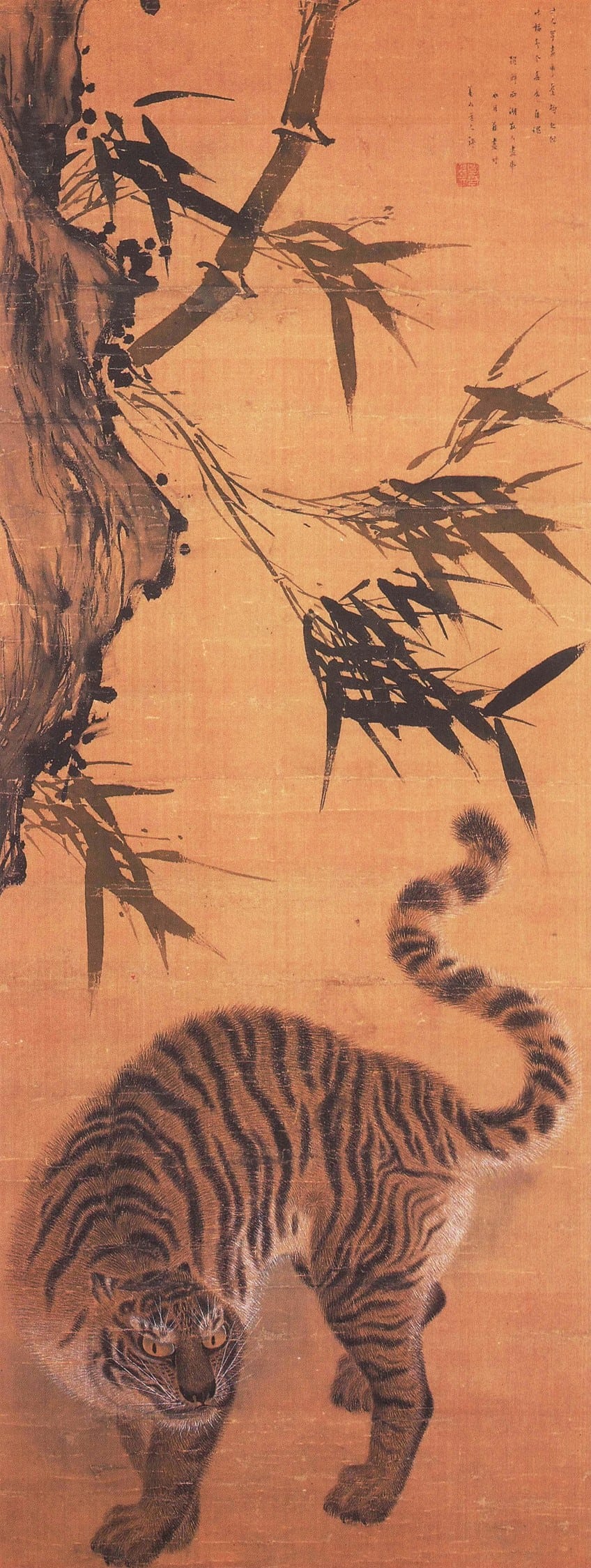

The iconic beast depicted in the painting is said to have been created by Sim Sa-Jeong, whose signature and pen name on the painting appear as Hyeonjae. The true identity of the artist behind the painting is an ongoing subject of debate with many scholars arguing that the calligraphic style does not match that of the other works of Sim Sa-Jeong.
The calculated tiger is presented as cautious, as if on the hunt, and occupies the majority of the page with its S-shaped figure.
The artist used a fine brush to render the fur of the creature, which was a common practice in many later Joseon-era animal paintings. The style of the tiger painting appears quite animated and leaves a lasting impression on the viewer since it is unlike any other traditional Korean painting of a tiger.
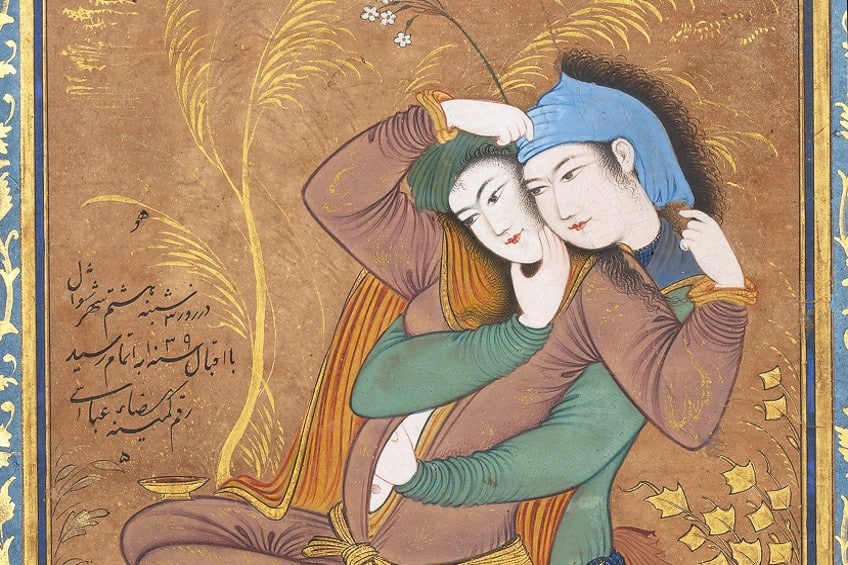
The Lovers (1630) by Riza-yi ‘Abbasi
| Artist | Riza-yi ‘Abbasi (1565 – 1635) |
| Date | 1630 |
| Medium | Opaque watercolor, ink, and gold on paper |
| Dimensions (cm) | 17.5 x 11.1 |
| Where It Is Housed | The Metropolitan Museum of Art, New York City, United States |
This famous Iranian painting by Riza-yi ‘Abbasi is an example of a revolutionary shift in Persian painting made evident in Abbasi’s style, use of color, and calligraphy. The Lovers was created around 1630 in the latter stages of his career at the Safavid court. This coincided with the period in Iran when the morals of society were “relaxed” under the rulership of Shah Safi.
The painting illustrates an entwined couple engaging in sexual foreplay while demonstrating the lack of expression on their faces, which was a common practice in figural paintings at the time.
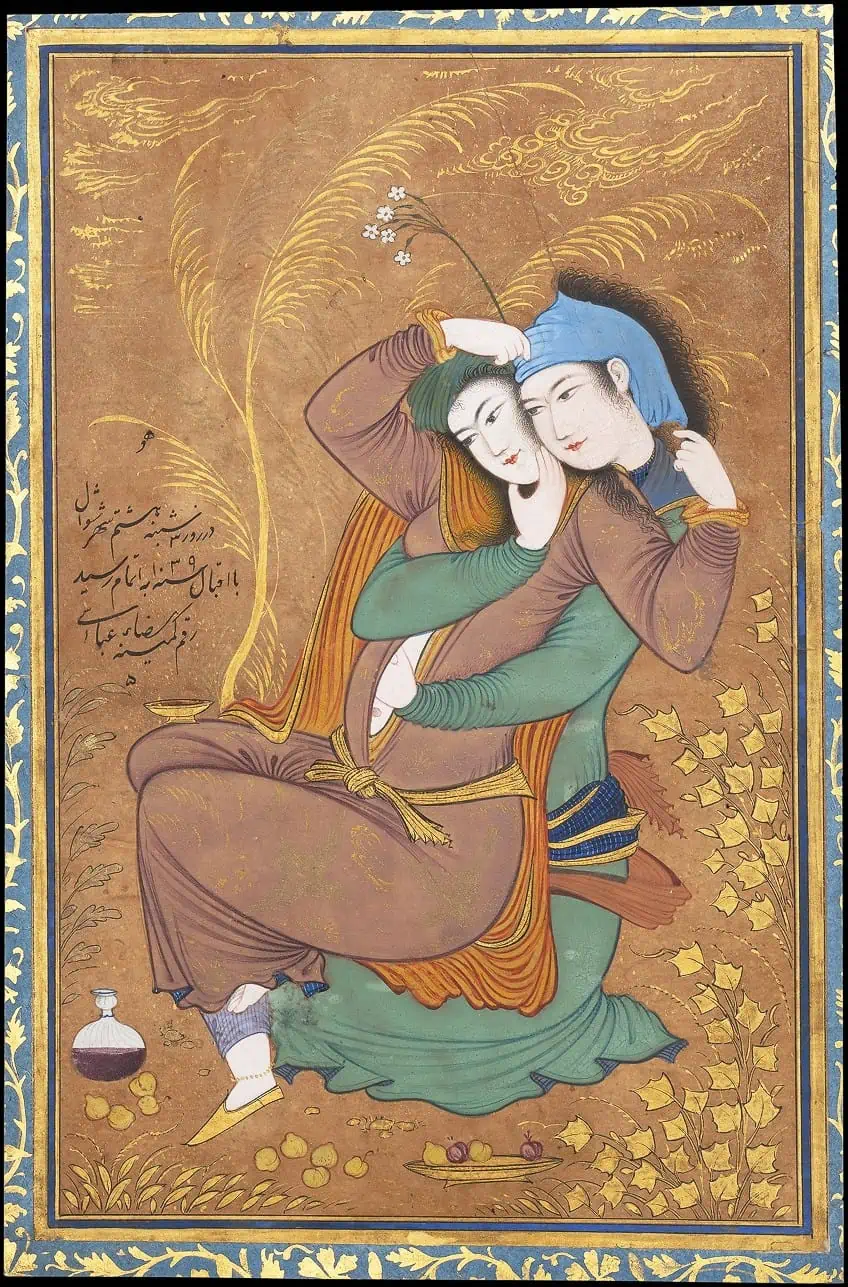

The toffee-colored drapery on the woman stands out and is often seen in his later works. Elements of pleasure are scattered in the scene, with the wine glass and pieces of fruit. It is believed that the woman was a prostitute whose name was undocumented. Prostitution in the mid-1600s in Safavid Iran was taxed by the government and served as one of the leading sources of income for the system.
Perhaps considered a Contemporary piece, The Lovers differs from previous traditional Asian artworks from the Near East since ancient subjects revolved around the relationships between humans and divine beings, including major war events, heroic tales, and votive sculpture.
Top Five Most Famous Asian Paintings From Contemporary History
Asian art also encountered influences from the West and other parts of the world while integrating artistic trends from other parts of Asia itself. Traditional Asian art demonstrates the essence of tradition, culture, religion, and artistic practice that reflects the interconnectedness of the world in ancient history. Below, we will explore some of the most famous Asian paintings from our Contemporary era that illustrates the boldness of Asian art and how it has shifted over the centuries.
The Dreamer (1955) by Pan Yuliang
| Artist | Pan Yuliang (Zhang Yuliang) (1895 – 1977) |
| Date | 1955 |
| Medium | Ink and color on paper |
| Dimensions (cm) | 54.5 x 32.5 |
| Where It Is Housed | Private Collection in France |
The Dreamer by Pan Yuliang is one of the most famous Modern Asian paintings by one of the most talented artists of the 20th century. Pan Yuliang, also known as Zhang Yuiliang, specialized in female nude paintings and self-portraits, often alluding to themes of maternity, beauty, health, and vitality in women.
From an early age, Pan Yuliang was sadly sold off to a brothel and became a prostitute. She then married and was supported by her husband to pursue art.
Pan went on to study in Shanghai and then in France and Rome where she honed her skills. Pan was an expert Expressionist and Realist painter who skillfully blended the traditional Chinese painting styles with Western approaches to create her signature style. The public at the time of this painting was averse to nudity and was severely criticized as being too vulgar and “cheap”.
However, the strong confidence in her line work, the female nude, as well as her unique sketch-like style in the painting are what give her paintings a contemporary edge.
Rain on the Pacific (1979) by Yayoi Kusama
| Artist | Yayoi Kusama (1929 – Present) |
| Date | 1979 |
| Medium | Enamel and ink on paperboard |
| Dimensions (cm) | 27 x 24 |
| Where It Is Housed | Private Collection |
Rain on the Pacific is a famous painting by Yayoi Kusama, a Japanese artist whose work spans the visual arts, including installation, sculpture, painting, video art, performance, and fashion. Kusama’s practice is often described as Minimalist and conceptual fused with autobiographical, sexual, and psychological content. Kusama attended the Kyoto City University of Arts where she trained in nihonga painting.
Nihonga painting is a traditional Japanese painting technique that was developed around the early 20th century and is created on washi paper or silk using brushes.
Nihonga paintings are typically either monochrome or polychrome with specific pigments for each. By the mid-20th century, Kusama had also begun her exploration of Abstract art through natural forms and started her definitive art style by covering objects and people in polka dots, which she referred to as “infinity nets”.
Kusama’s trademarked polka dots make an appearance in Rain on the Pacific through the scattered splotches of ink in red and black, colors which can be seen in later artworks featuring the polka dot in Kusama’s work.
Untitled (After “Gandhi”), also known as The Attenborough Panels (c. 1983) by Maqbool Fida Husain
| Artist | Maqbool Fida Husain (1915 – 2011) |
| Date | 1983 |
| Medium | Acrylic on canvas |
| Dimensions (cm) | 228.6 × 81.3 |
| Where It Is Housed | Aicon Gallery, New York, United States |
This famous Contemporary Asian painting by Indian artist Maqbool Fida Husain is a unique work that was created by the artist after being inspired by the 1982 biopic Gandhi by Sir Richard Attenborough. Mahatma Gandhi served as an inspirational figure for Husain who regarded the political figure as the “Mother Teresa” of his art. The painting consists of six panels each representing key moments in Gandhi’s life and career.
The final panel on the far right is one of the most elusive panels since its depiction of Gandhi is not clear yet he is defined by his dhoti (loincloth).
Husain’s introduction to painting began in his early career in billboard illustrations for feature films as well as furniture and toy designing. As his art career progressed, he explored themes that combined traditional Indian folklore with mythical and tribal art to produce Cubist-styled Contemporary paintings such as this Gandhi-inspired one.
Maqbool Fida Husain is considered one of the best rising Modern and Contemporary artists to look out for.
727 (1996) by Takashi Murakami
| Artist | Takashi Murakami (1962 – Present) |
| Date | 1996 |
| Medium | Acrylic on canvas mounted on board, three panels |
| Dimensions (cm) | 299.7 x 449.6 |
| Where It Is Housed | The Museum of Modern Art, New York City, United States |
Takashi Murakami is one of the most famous Asian Contemporary artists who had collaborated with many major luxury fashion brands, including Louis Vuitton’s late Virgil Abloh. Murakami is regarded as the “Warhol of Asia” and is most famous for his contribution to Contemporary Pop art and the Superflat Post-Modern art movement.
727 is an acrylic-on-canvas painting mounted on three large panels depicting a stylized wave with a visceral purple-blue tinted background.
An anime-like creature is at the center of this surreal painting and is seen riding the wave with its glistening red eyes and gleeful smile. The round frame of the creature contains the letters “DOB” and is affiliated with Mr. DOB, which Murakami created in 1993 as an anime character inspired by manga and anime in post-war Japan.
Mr. DOB is Murakami’s alter ego, which morphs into different forms.
The background of the painting is informed by nihonga painting, achieved by sanding down almost 20 layers of acrylic paint. This famous painting is a precursor to Murakami’s theory of the Superflat movement in 2000, which marked the culmination of fine art and Pop consumerism into one entity as a plane not “bound by limits or the system…as a blank slate”.
Les Brumes Du Passé (2004) by Chu Teh-Chun
| Artist | Chu Teh-Chun (1920 – 2014) |
| Date | 2004 |
| Medium | Oil on canvas |
| Dimensions (cm) | 130 x 195 |
| Where It Is Housed | Important Private Asian Collection |
Internationally acclaimed Chinese-French Abstraction artist, Chu Teh-Chun, was one of the leading Contemporary Asian artists of the 20th and 21st centuries. Chu The-Chun was a pioneering artist who championed the art style of combining Western Abstract art styles with traditional Chinese art and produced this famous painting, Les Brumes Du Passé in 2004.
Bridging the gap between France and China, Chu Teh-Chun led the integration of both cultures and became the first Chinese member of the Académie des Beaux-Arts.
His paintings are described as rhythmic and nuanced with a unique blend of colors that evoke a sense of harmony and movement. Imagination played a major role in the painting approach that Chu used to distill the essence from the mundane.
One could go on and on about the various imaginative and creative art forms and techniques produced in Asia that have informed and inspired the artworks and artists of the Contemporary era. We hope that this article has inspired you to further explore the very rich and dynamic world of Asian art, from ancient times to modern-day society.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is Asian Art?
Asian art is art that is produced within Asia or by artists of Asian descent, incorporating traditional Asian art practices into Contemporary art processes. Asian art includes numerous traditional art forms such as calligraphy, pottery, sculpture, painting, decorative arts, textile art, architecture, design, and performance. Ancient Asian art also encompasses art from regions that extend into the Near East.
What Are the Characteristics of Asian Art?
The characteristics of Asian art include multiple factors that contribute to the specific regional and cultural aesthetics of art from different regions in Asia. The most prominent characteristics found in art from Asia include influences from Buddhism, Chinese culture, ink-wash painting, calligraphy as a separate art form, religious subjects, mythical characters and narratives, landscape paintings, and imagery containing auspicious symbols. These characteristics are still considered broad since each region was influenced by previous and/or surrounding cultures.
Who Is the Most Famous Asian Painter?
Gu Kaizhi is considered to be the most famous Asian painter in the history of Asian art. Gu Kaizhi was an iconic Chinese painter and one of the most revered artists of ancient China who was also a politician, calligrapher, and poet.
Jordan Anthony is a Cape Town-based film photographer, curator, and arts writer. She holds a Bachelor of Art in Fine Arts from the University of the Witwatersrand, Johannesburg, where she explored themes like healing, identity, dreams, and intuitive creation in her Contemporary art practice. Jordan has collaborated with various local art institutions, including the KZNSA Gallery in Durban, the Turbine Art Fair, and the Wits Art Museum. Her photography focuses on abstract color manipulations, portraiture, candid shots, and urban landscapes. She’s intrigued by philosophy, memory, and esotericism, drawing inspiration from Surrealism, Fluxus, and ancient civilizations, as well as childhood influences and found objects. Jordan is working for artfilemagazine since 2022 and writes blog posts about art history and photography.
Learn more about Jordan Anthony and about us.
Cite this Article
Jordan, Anthony, “Famous Asian Paintings – A Closer Look at Ancient Asian Art.” artfilemagazine – Your Online Art Source. January 13, 2023. URL: https://artfilemagazine.com/famous-asian-paintings/
Anthony, J. (2023, 13 January). Famous Asian Paintings – A Closer Look at Ancient Asian Art. artfilemagazine – Your Online Art Source. https://artfilemagazine.com/famous-asian-paintings/
Anthony, Jordan. “Famous Asian Paintings – A Closer Look at Ancient Asian Art.” artfilemagazine – Your Online Art Source, January 13, 2023. https://artfilemagazine.com/famous-asian-paintings/.